Knowledge Distillation: A Review of Methods and Applications in LiDAR Data
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v13i11.7589Keywords:
Knowledge distillation, LiDAR, Autonomous Systems, Object Detection, Semantic Segmentation, Point CloudsAbstract
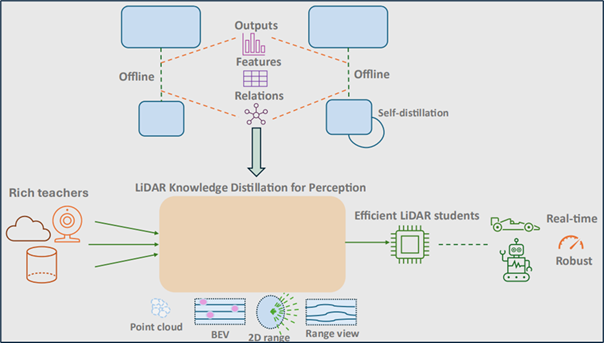
Knowledge distillation (KD) is a machine learning technique where a compact student model is trained by a larger teacher model to create efficient, high-performance models suitable for devices with limited computational resources. The student learns by mimicking the teacher’s nuanced predictions, known as ”soft targets”, which provide a richer learning signal than traditional ground-truth labels. Methods are categorized by the source of knowledge—such as the teacher’s final outputs (response-based), intermediate features (feature-based), or the relationships between data points (relation-based)—and by the training strategy, including offline, online, and self-distillation schemes. This review focuses on the application of KD to 2D and 3D LiDAR data for tasks like object detection and semantic segmentation in autonomous systems. In this domain, knowledge distillation is critical for developing lightweight models that can run in real-time, enabling cross-modal learning from expensive LiDAR to cheaper sensors, and addressing inherent challenges of point cloud data such as sparsity and sensor-specific domain gaps.
References
[1] G. Hinton, O. Vinyals, and J. Dean, “Distilling the knowledge in a neural network,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1503.02531, 2015.
[2] C. Bucilua, R. Caruana, and A. Niculescu-Mizil, “Model compression,” Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, ACM, pp.535-541, 2006.
[3] A. Romero, N. Ballas, S. E. Kahou, A. Chassang, C. Gatta, and Y. Bengio, “FitNets: Hints for thin deep nets,” arXiv preprint, 2015.
[4] A. M. Mansourian, A. Jalali, R. Ahmadi, and S. Kasaei, “Attention-guided feature distillation for semantic segmentation,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.05451, 2024.
[5] W. Park, D. Kim, Y. Lu, and M. Cho, “Relational knowledge distillation,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.3967–3976, 2019.
[6] A. M. Mansourian, R. Ahmadi, M. Ghafouri, A. M. Babaei, E. B. Golezani, Z. Y. Ghamchi, V. Ramezanian, A. Taherian, K. Dinashi, A. Miri, et al., “A comprehensive survey on knowledge distillation,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.12067, 2025.
[7] BhavyaShree P, Sharon Thomas Takri, R. Gurunath, "A Comparative Study of Enabling Technologies for Autonomous Vehicles", International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.07, Special Issue.09, pp.9-11, 2019.
[8] Nupur Choudhury, Rupesh Mandal2, "A survey on Robotic Vehicles in Autonomous Navigation", International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.3, Issue.5, pp.79-84, 2015.
[9] Z. Liu, X. Qi, and C.-W. Fu, “3D-to-2D distillation for indoor scene parsing,” CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE/CVF, pp.4462–4472, 2021.
[10] Y. Wei, Z. Wei, Y. Rao, J. Li, J. Zhou, and J. Lu, “LiDAR distillation: Bridging the beam-induced domain gap for 3D object detection,” European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, pp.179–195, 2022.
[11] Z. Wang, D. Li, C. Luo, C. Xie, and X. Yang, “DistillBEV: Boosting multi-camera 3D object detection with cross-modal knowledge distillation,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE/CVF, pp.8637–8646, 2023.
[12] S. Zhou, W. Liu, C. Hu, S. Zhou, and C. Ma, “UniDistill: A universal cross-modality knowledge distillation framework for 3D object detection in bird’s-eye view,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.5116–5125, 2023.
[13] J. Li, M. Lu, J. Liu, Y. Guo, L. Du, and S. Zhang, “BEV-LGKD: A unified LiDAR-guided knowledge distillation framework for BEV 3D object detection,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.00623, 2022.
[14] T. Jiao, Y. Chen, Z. Zhang, C. Guo, and J. Song, “MMDistill: Multi-modal BEV distillation framework for multi-view 3D object detection,” Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.81, Issue.3, 2024. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2024.058238.
[15] F. Jiang, H. Gao, S. Qiu, H. Zhang, R. Wan, and J. Pu, “Knowledge distillation from 3D to bird’s-eye-view for LiDAR semantic segmentation,” 2023 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), IEEE, pp.402–407, 2023.
[16] H. Zhao, Q. Zhang, S. Zhao, Z. Chen, J. Zhang, and D. Tao, “SimDistill: Simulated multi-modal distillation for BEV 3D object detection,” Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI Press, Vol.38, pp.7460–7468, 2024.
[17] S. Xu, F. Li, P. Huang, Z. Song, and Z.-X. Yang, “TIGDistill-BEV: Multi-view BEV 3D object detection via target inner-geometry learning distillation,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.20911, 2024.
[18] L. Zhao, J. Song, and K. A. Skinner, “CRKD: Enhanced camera-radar object detection with cross-modality knowledge distillation,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.15470–15480, 2024.
[19] L. Zhang, R. Dong, H.-S. Tai, and K. Ma, “PointDistiller: Structured knowledge distillation towards efficient and compact 3D detection,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.21791–21801, 2023.
[20] L. T. Hai, T. D. Le, Z. Ding, Q. Tian, and T.-S. Hy, “Topology-guided knowledge distillation for efficient point cloud processing,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.08101, 2025.
[21] Y. Hou, X. Zhu, Y. Ma, C. C. Loy, and Y. Li, “Point-to-voxel knowledge distillation for LiDAR semantic segmentation,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.8479–8488, 2022.
[22] S. J. Sanjay, J. Akash, A. S. Dimple, et al., “Adversarial learning based knowledge distillation on 3D point clouds,” 2025 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), IEEE, pp.2932–2941, 2025.
[23] Y. Zhang, Y. Qu, Y. Xie, Z. Li, S. Zheng, and C. Li, “Perturbed self-distillation: Weakly supervised large-scale point cloud semantic segmentation,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE/CVF, pp.15520–15528, 2021.
[24] J. Li, H. Dai, and Y. Ding, “Self-distillation for robust LiDAR semantic segmentation in autonomous driving,” European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, pp.659–676, 2022.
[25] C. Sautier, G. Puy, S. Gidaris, A. Boulch, A. Bursuc, and R. Marlet, “Image-to-LiDAR self-supervised distillation for autonomous driving data,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.9891–9901, 2022.
[26] A. Gambashidze, A. Dadukin, M. Golyadkin, M. Razzhivina, and I. Makarov, “Weak-to-strong 3D object detection with X-ray distillation,” arXiv preprint, 2024.
[27] X. Huang, H. Wu, X. Li, X. Fan, C. Wen, and C. Wang, “Sunshine to rainstorm: Cross-weather knowledge distillation for robust 3D object detection,” Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI Press, Vol.38, pp.2409–2416, 2024.
[28] A. Umam, C.-K. Yang, M.-H. Chen, J.-H. Chuang, and Y.-Y. Lin, “PartDistill: 3D shape part segmentation by vision-language model distillation,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.3470–3479, 2024.
[29] D. Jia, A. Hermans, and B. Leibe, “DR-SPAAM: A spatial-attention and auto-regressive model for person detection in 2D range data,” International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), IEEE, 2020.
[30] H. Yang, Y. Yang, C. Yao, C. Liu, and Q. Chen, “Li2Former: Omni-dimension aggregation transformer for person detection in 2-D range data,” IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, Vol.73, 2024. 10.1109/TIM.2024.3420353.
[31] L. Beyer, A. Hermans, and B. Leibe, “DROW: Real-time deep learning based wheelchair detection in 2D range data,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), Vol.2, Issue.2, pp.585-592, 2016. 10.1109/LRA.2016.2645131.
[32] L. Beyer, A. Hermans, T. Linder, K. O. Arras, and B. Leibe, “Deep person detection in 2D range data,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), Vol.3, Issue.3, pp.2726-2733, 2018. 10.1109/LRA.2018.2835510.
[33] R. Martin-Martin, M. Patel, H. Rezatofighi, A. Shenoi, J. Gwak, E. Frankel, A. Sadeghian, and S. Savarese, “JRDB: A dataset and benchmark of egocentric robot visual perception of humans in built environments,” IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol.45, Issue.6, pp.6748–6765, 2021. 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3070543.
[34] F. Amodeo, N. Pérez-Higueras, L. Merino, and F. Caballero, “FROG: A new people detection dataset for knee-high 2D range finders,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.08531, 2023.
[35] P. Sun, H. Kretzschmar, X. Dotiwalla, A. Chouard, V. Patnaik, P. Tsui, J. Guo, Y. Zhou, Y. Chai, B. Caine, V. Vasudevan, W. Han, J. Ngiam, H. Zhao, A. Timofeev, S. Ettinger, M. Krivokon, A. Gao, A. Joshi, Y. Zhang, J. Shlens, Z. Chen, and D. Anguelov, “Scalability in perception for autonomous driving: Waymo Open Dataset,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.04838, 2019.
[36] B. Yang, T. Tao, W. Wu, Y. Zhang, X. Meng, and J. Yang, “MultiDistiller: Efficient multimodal 3D detection via knowledge distillation for drones and autonomous vehicles,” Drones, Vol.9, Issue.5, pp.322, 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9050322.
[37] B. Zhao, Q. Cui, R. Song, Y. Qiu, and J. Liang, “Decoupled knowledge distillation,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.11953–11962, 2022.
[38] Z. Chi, T. Zheng, H. Li, Z. Yang, B. Wu, B. Lin, and D. Cai, “NormKD: Normalized logits for knowledge distillation,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.00520, 2023.
[39] J. Guo, M. Chen, Y. Hu, C. Zhu, X. He, and D. Cai, “Reducing the teacher-student gap via spherical knowledge distillation,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.07485, 2020.
[40] B. B. Sau and V. N. Balasubramanian, “Deep model compression: Distilling knowledge from noisy teachers,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1610.09650, 2016.
[41] M. Yuan, B. Lang, and F. Quan, “Student-friendly knowledge distillation,” Knowledge-Based Systems, Vol.296, pp.111915, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2024.111915.
[42] J. Yang, S. Shi, R. Ding, Z. Wang, and X. Qi, “Towards efficient 3D object detection with knowledge distillation,” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Curran Associates, Vol.35, pp.21300–21313, 2022.
[43] S. Kim, Y. Kim, S. Hwang, H. Jeong, and D. Kum, “LabelDistill: Label-guided cross-modal knowledge distillation for camera-based 3D object detection,” European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, pp.19–37, 2024.
[44] S. Zagoruyko, N. Komodakis, “Paying More Attention to Attention: Improving the Performance of Convolutional Neural Networks via Attention Transfer,”, arXiv preprint arXiv: 1612.03928, 2016.
[45] B. Heo, M. Lee, S. Yun, and J. Y. Choi, “Knowledge transfer via distillation of activation boundaries formed by hidden neurons,” Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI Press, Vol.33, pp.3779–3787, 2019.
[46] Z. Huang and N. Wang, “Like what you like: Knowledge distill via neuron selectivity transfer,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.01219, 2017.
[47] J. Kim, S. Park, and N. Kwak, “Paraphrasing complex network: Network compression via factor transfer,” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Curran Associates, Vol.31, 2018.
[48] B. Heo, J. Kim, S. Yun, H. Park, N. Kwak, and J. Y. Choi, “A comprehensive overhaul of feature distillation,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE/CVF, pp.1921–1930, 2019.
[49] C. Shu, Y. Liu, J. Gao, Z. Yan, and C. Shen, “Channel-wise knowledge distillation for dense prediction,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE/CVF, pp.5311–5320, 2021.
[50] Z. Yang, Z. Li, M. Shao, D. Shi, Z. Yuan, and C. Yuan, “Masked generative distillation,” European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, pp.53–69, 2022.
[51] Z. Liu, Y. Wang, X. Chu, N. Dong, S. Qi, and H. Ling, “A simple and generic framework for feature distillation via channel-wise transformation,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE/CVF, pp.1129–1138, 2023.
[52] T. Huang, Y. Zhang, M. Zheng, S. You, F. Wang, C. Qian, and C. Xu, “Knowledge diffusion for distillation,” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Curran Associates, Vol.36, pp.65299–65316, 2023.
[53] T. Liu, C. Chen, X. Yang, and W. Tan, “Rethinking knowledge distillation with raw features for semantic segmentation,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, IEEE/CVF, pp.1155–1164, 2024.
[54] Y. Chen, Y. Xian, A. Koepke, Y. Shan, and Z. Akata, “Distilling audio-visual knowledge by compositional contrastive learning,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.7016–7025, 2021.
[55] P. Chen, S. Liu, H. Zhao, and J. Jia, “Distilling knowledge via knowledge review,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.5008–5017, 2021.
[56] S. Tong, Z. Xia, A. Alahi, X. He, and Y. Shi, “GeoDistill: Geometry-guided self-distillation for weakly supervised cross-view localization,” arXiv preprint, 2025.
[57] S. Qiu, F. Jiang, H. Zhang, X. Xue, and J. Pu, “Multi-to-single knowledge distillation for point cloud semantic segmentation,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.14800, 2023.
[58] J. Yim, D. Joo, J. Bae, and J. Kim, “A gift from knowledge distillation: Fast optimization, network minimization and transfer learning,” Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, pp.4133–4141, 2017.
[59] L. Liu, Q. Huang, S. Lin, H. Xie, B. Wang, X. Chang, and X. Liang, “Exploring inter-channel correlation for diversity-preserved knowledge distillation,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE/CVF, pp.8271–8280, 2021.
[60] C. Wang, J. Zhong, Q. Dai, Y. Qi, Q. Yu, F. Shi, R. Li, X. Li, and B. Fang, “Channel correlation distillation for compact semantic segmentation,” International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, Vol.37, Issue.03, pp.2350004, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218001423500040.
[61] F. Tung and G. Mori, “Similarity-preserving knowledge distillation,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE/CVF, pp.1365–1374, 2019.
[62] C. Yang, H. Zhou, Z. An, X. Jiang, Y. Xu, and Q. Zhang, “Cross-image relational knowledge distillation for semantic segmentation,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.12319–12328, 2022.
[63] Y. Feng, X. Sun, W. Diao, J. Li, and X. Gao, “Double similarity distillation for semantic image segmentation,” IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, Vol.30, Issue.pp.5363–5376, 2021. 10.1109/TIP.2021.3083113.
[64] T. Huang, S. You, F. Wang, C. Qian, and C. Xu, “Knowledge distillation from a stronger teacher,” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Curran Associates, Vol.35, pp.33716–33727, 2022.
[65] Y. Liu, K. Chen, C. Liu, Z. Qin, Z. Luo, and J. Wang, “Structured knowledge distillation for semantic segmentation,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.2604–2613, 2019.
[66] L. Zhang and K. Ma, “Structured knowledge distillation for accurate and efficient object detection,” IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol.45, Issue.12, pp.15706–15724, 2023. 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3300470.
[67] W. Yan, L. Xu, H. Liu, C. Tang, and W. Zhou, “High-order structural relation distillation networks from LiDAR to monocular image 3D detectors,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, Vol.9, Issue.2, pp.3593–3604, 2023. 10.1109/TIV.2023.3341981.
[68] C. B. Rist, M. Enzweiler, and D. M. Gavrila, “Cross-sensor deep domain adaptation for LiDAR detection and segmentation,” 2019 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), IEEE, pp.1535–1542, 2019.
[69] S. Zhang, J. Deng, L. Bai, H. Li, W. Ouyang, and Y. Zhang, “HVDistill: Transferring knowledge from images to point clouds via unsupervised hybrid-view distillation,” arXiv preprint, 2024.
[70] K. Ning, Y. Liu, Y. Su, and K. Jiang, “Diversity knowledge distillation for LiDAR-based 3-D object detection,” IEEE Sensors Journal, Vol.23, Issue.11, pp.11181–11193, 2023. 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3241624.
[71] S. Wang, W. Li, W. Liu, X. Liu, and J. Zhu, “LiDAR2Map: In defense of LiDAR-based semantic map construction using online camera distillation,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.5186–5195, 2023.
[72] X. Yan, J. Gao, C. Zheng, C. Zheng, R. Zhang, S. Cui, and Z. Li, “2Dpass: 2D priors assisted semantic segmentation on LiDAR point clouds,” European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, pp.677–695, 2022.
[73] H. Cho, J. Choi, G. Baek, and W. Hwang, “ITKD: Interchange transfer-based knowledge distillation for 3D object detection,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.13540–13549, 2023.
[74] Y. Guo, Y. Li, D. Ren, X. Zhang, J. Li, L. Pu, C. Ma, X. Zhan, J. Guo, M. Wei, et al., “LidarNet: A real-scanned 3D point cloud dataset for indoor scenes,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.21989–21999, 2024.
[75] C. Stearns, A. Fu, J. Liu, J. J. Park, D. Rempe, D. Paschalidou, and L. J. Guibas, “CurveCloudNet: Processing point clouds with 1D structure,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE/CVF, pp.27981–27991, 2024.
[76] H. Jing, A. Wang, Y. Zhang, D. Bu, and J. Hou, “Reflectance prediction-based knowledge distillation for robust 3D object detection in compressed point clouds,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.17442, 2025.
[77] J. Zhang and J. Liu, “Voxel-to-Pillar: Knowledge distillation of 3D object detection in point cloud,” Proceedings of the 4th European Symposium on Software Engineering, pp.99–104, 2023.
[78] Y. Liu, L. Kong, J. Cen, R. Chen, W. Zhang, L. Pan, K. Chen, and Z. Liu, “Segment any point cloud sequences by distilling vision foundation models,” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Curran Associates, Vol.36, pp.37193–37229, 2023.
[79] B. Wu, X. Zhou, S. Zhao, X. Yue, and K. Keutzer, “SqueezeSegV2: Improved model structure and unsupervised domain adaptation for road-object segmentation from a LiDAR point cloud,” 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), IEEE, pp.4376–4382, 2019.
[80] A. Milioto, I. Vizzo, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “RangeNet++: Fast and accurate LiDAR semantic segmentation,” 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), IEEE, pp.4213–4220, 2019.
[81] N. Kim and J. An, “Knowledge distillation for traversable region detection of LiDAR scan in off-road environments,” Sensors, Vol.24, Issue.1, pp.79, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24010079.
[82] E. Son, J. Choi, J. Song, Y. Jin, and S. J. Lee, “Monocular depth estimation from a fisheye camera based on knowledge distillation,” Sensors, Vol.23, Issue.24, pp.9866, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23249866.
[83] A. Mahmoud, A. Harakeh, and S. Waslander, “Image-to-LiDAR relational distillation for autonomous driving data,” European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, pp.459–475, 2024.
[84] S. Lahlali, S. Kara, H. Ammar, F. Chabot, N. Granger, H. Le Borgne, and Q.-C. Pham, “XMoD: Cross-modal distillation for 2D/3D multi-object discovery from 2D motion,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.15022, 2025.
[85] H. Govindarajan, M. K. Wozniak, M. Klingner, C. Maurice, B. R. Kiran, and S. Yogamani, “CleverDistiller: Simple and spatially consistent cross-modal distillation,” arXiv preprint, 2025.
[86] H. Caesar, V. Bankiti, A. H. Lang, S. Vora, V. Liong, Q. Xu, A. Krishnan, Y. Pan, G. Baldan, and O. Beijbom, “nuScenes: A multimodal dataset for autonomous driving,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE/CVF, pp.11618–11628, 2020
[87] N. Silberman, D. Hoiem, P. Kohli, and R. Fergus, “Indoor segmentation and support inference from RGBD images,” Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Springer, pp.746–760, 2012.
[88] S. Song, S. Lichtenberg, and J. Xiao, “SUN RGB-D: A RGB-D scene understanding benchmark suite,” Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, pp.567–576, 2015.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




