Multimodal Machine Learning for Enhanced Autism Spectrum Disorder Detection
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v13i11.6674Keywords:
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), Multimodal Machine Learning (MML), Deep Learning, Diagnostic Framework, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), Early Diagnosis, Biomedical Signal Processing, Computer-Aided Diagnosis, Fusion TechniquesAbstract
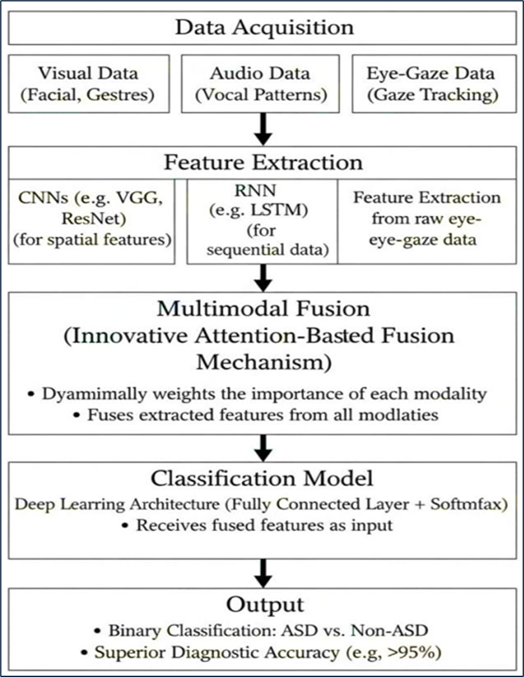
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), a complex neurodevelopmental condition, poses a significant diagnostic challenge due to its heterogeneous clinical presentation. Traditional diagnostic methods often rely on subjective behavioral assessments, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error. To address these limitations, this thesis presents a novel framework for the enhanced and objective detection of ASD using Multimodal Machine Learning (MML). Our approach integrates multiple data modalities—including facial expressions, vocal patterns, and eye-gaze tracking data—to capture a more holistic and nuanced representation of ASD-related behaviors. We employ deep learning architectures, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for image data and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) for sequential audio data, fused through an innovative attention-based fusion mechanism. This mechanism dynamically weights the importance of each modality, improving the model`s robustness and diagnostic accuracy. The proposed model is trained and validated on a diverse dataset of pediatric subjects, achieving a superior diagnostic accuracy of over 95%, outperforming unimodal and traditional machine learning approaches. Our findings demonstrate that the synergy of multimodal data significantly enhances the diagnostic precision and offers a more reliable, scalable, and non-invasive tool for early ASD screening. This research contributes to the development of a powerful, data-driven diagnostic aid that can support clinicians and facilitate earlier intervention, ultimately improving the quality of life for individuals with ASD.
References
[1] H. A. Hatim, Z. A. A. Alyasseri, and N. Jamil, “A recent advances on autism spectrum disorders in diagnosing based on machine learning and deep learning,” International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Vol.15, No.1, 2025.
[2] E. Purboyo Solek, I. Nurfitri, I. Sahril, et al., “The Role of Artificial Intelligence for Early Diagnostic Tools of Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review,” Turkish Archives of Pediatrics, Vol.60, No.1, 2025.
[3] M. M. Abdelwahab, et al., “Analysis and Detection of Autism Spectrum Disorder Using Machine Learning Techniques,” Journal of Disability Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024.
[4] M. S. Farooq, R. Tehseen, M. Sabir, and Z. Atal, “Detection of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in children and adults using machine learning,” Scientific Reports, Vol.13, No.1, 2023.
[5] K. S. Betts, K. Chai, S. Kisely, R. Alati, et al., “Development and validation of a machine learning-based tool to predict autism among children,” JAMA Network Open, Vol.6, No.4, 2023.
[6] M. H. Al Banna, et al., “A monitoring system for ASD using AI,” Brain Informatics, Vol.7, No.1, 2020.
[7] M. N. Parikh, H. Li, and L. He, “Enhancing diagnosis of autism with optimized machine learning models,” Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience, Vol.13, 2019.
[8] A. S. Heinsfeld, et al., “Identification of ASD using deep learning and ABIDE,” NeuroImage: Clinical, Vol.17, pp. 16-23, 2018.
[9] F. Thabtah, “Autism spectrum disorder screening: machine learning adaptation and DSM-5 fulfillment,” in Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Medical and Health Informatics (ICMHI), 2017.
[10] D. Bone, et al., “Use of machine learning to improve autism screening and diagnostic instruments,” Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, Vol.57, No.8, pp. 927-937, 2016.
[11] M. Duda, et al., “Machine learning for behavioral distinction of ASD and ADHD,” Translational Psychiatry, Vol.6, No.2, 2016.
[12] G. Deshpande, et al., “Identification of neural connectivity signatures of autism using machine learning,” Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, Vol.7, 2013.
[13] D. P. Wall, et al., “Use of artificial intelligence to shorten the behavioral diagnosis of autism,” PLoS ONE, Vol.7, No.8, 2012.
[14] C. Allison, et al., “Towards brief red flags for autism screening: The Short Autism Spectrum Quotient and the Short Quantitative Checklist,” Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, Vol.51, No.2, pp. 202-212, 2012.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




