Deep Feature Fusion for Enhanced Medical Image Retrieval Using CNN and Texture Descriptors
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v13i11.4552Keywords:
Medical Image Retrieval, Deep Learning, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Feature Fusion, Local Binary Pattern (LBP), Gabor Filter, Texture Descriptors, Content-Based Image Retrieval (CBIR), Similarity MetricsAbstract
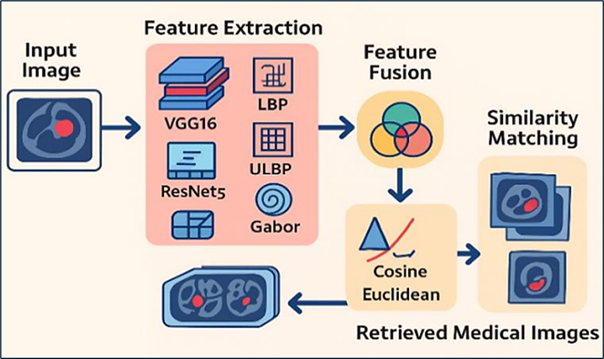
Medical image retrieval is an important tool for supporting doctors in identifying diseases. Earlier systems mainly used handcrafted features like color and texture, but such features often fail to capture the complex patterns in medical images. In this paper, we present a hybrid method that combines deep features from pretrained CNN models with traditional texture-based features like Local Binary Pattern (LBP) and Gabor filters. By merging deep learning with texture descriptors, our approach enhances the quality of image retrieval. Experiments are performed on popular medical dataset like BreakHis and various distance metrics such as Euclidean and Cosine are used for similarity comparison. The results show that our fusion-based system performs better than standard techniques in terms of precision and retrieval accuracy. This confirms the usefulness of combining deep features with handcrafted features for improving medical image search systems.
References
[1] K. Simonyan and A. Zisserman, “Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556, 2014.
[2] K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, and J. Sun, “Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition,” Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp.770–778, 2016.
[3] T. Ojala, M. Pietikäinen, and D. Harwood, “A Comparative Study of Texture Measures with Classification Based on Featured Distributions,” Pattern Recognition, Vol.29, No.1, pp.51–59, 1996.
[4] M. Tuceryan and A. K. Jain, “Texture Analysis,” Handbook of Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision, World Scientific, pp.207–248, 1998.
[5] M. Spanhol, L. Oliveira, C. Petitjean, and L. Heutte, “A Dataset for Breast Cancer Histopathological Image Classification,” IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, Vol.63, No.7, pp.1455–1462, July 2016.
[6] F. Chollet, “Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions,” Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp.1800–1807, 2017.
[7] G. Hinton, N. Srivastava, and K. Swersky, “Improving Neural Networks by Preventing Co-Adaptation of Feature Detectors,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1207.0580, 2012.
[8] S. Minaee, Y. Boykov, F. Porikli, A. Plaza, N. Kehtarnavaz, and D. Terzopoulos, “Image Segmentation Using Deep Learning: A Survey,” IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol.44, No.7, pp.3523–3542, July 2022.
[9] L. Zhang, S. Ding, and B. Du, “Medical Image Retrieval Using Convolutional Neural Network and Relevance Feedback,” Neurocomputing, Vol.284, pp.65–73, 2018.
[10] M. Kaur, M. Kaur, and G. Singh, “Hybrid Feature-Based Medical Image Retrieval System Using Convolutional Neural Network and LBP,” Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, Vol.42, No.1, pp.206–219, 2022.
[11] Z. Gu, J. Cheng, H. Fu, et al., “CE-Net: Context Encoder Network for 2D Medical Image Segmentation,” IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, Vol.38, No.10, pp.2281–2292, 2019.
[12] X. Li, H. Chen, X. Qi, Q. Dou, C. Fu, and P. Heng, “H-DenseUNet: Hybrid Densely Connected UNet for Liver and Tumor Segmentation from CT Volumes,” IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, Vol.37, No.12, pp.2663–2674, 2018.
[13] J. Kaur and A. Sharma, “Efficient Deep Learning Framework for Medical Image Classification,” International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering (IJCSE), Vol.12, Issue 10, pp.45–52, 2024.
[14] S. Kumar and R. Gupta, “An Improved Convolutional Neural Network Approach for Medical Image Retrieval,” International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering (IJCSE), Vol.13, Issue 2, pp.99–106, 2025.
[15] S. Bar, I. Diamant, L. Wolf, and H. Greenspan, “Deep learning with non-medical training used for chest pathology identification,” Medical Imaging 2015: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, 2015.
[16] A. Esteva, B. Kuprel, et al., “Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks,” Nature, Vol.542, pp.115–118, 2017.
[17] D. Shen, G. Wu, and H. Suk, “Deep learning in medical image analysis,” Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, Vol.19, pp.221–248, 2017.
[18] X. Wang, Y. Peng, L. Lu, et al., “ChestX-ray8: Hospital-scale chest X-ray database and benchmarks on weakly-supervised classification and localization,” CVPR, 2017.
[19] Y. Lecun, Y. Bengio, and G. Hinton, “Deep learning,” Nature, Vol.521, pp.436–444, 2015.
[20] K. G. Dhal, S. Ghosh, “A survey on content-based image retrieval using deep learning,” Journal of King Saud University – Computer and Information Sciences, 2022.
[21] L. Yang, P. Wang, et al., “Combining deep learning with hand-crafted features for medical image analysis,” Pattern Recognition Letters, 2020.
[22] A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, and G. Hinton, “ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks,” NIPS, 2012
[23] H. R. Roth, L. Lu, et al., “DeepOrgan: Multi-level deep convolutional networks for automated pancreas segmentation,” MICCAI, pp.556–564, 2015.
[24] M. Anthimopoulos, S. Christodoulidis, et al., “Lung pattern classification for interstitial lung diseases using a deep convolutional neural network,” IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2016.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




