Design and Implementation of a Secure Interoperable EHR System Using Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, and Decentralized IPFS Storage
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v13i11.2936Keywords:
Blockchain, Electronic Health Records, GDPR Compliance, Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, IPFS, Interoperability, Smart Contracts, Healthcare Data PrivacyAbstract
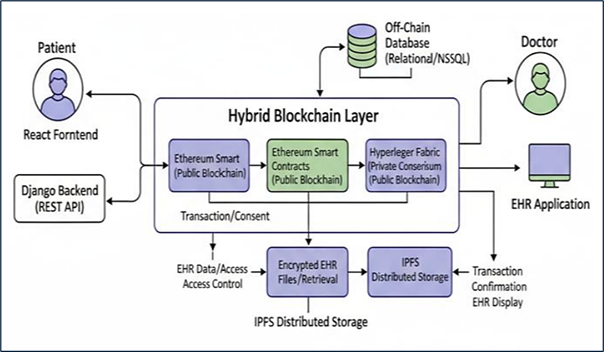
The rapid growth of digital healthcare has increased the demand for electronic health record (EHR) systems that ensure secure data exchange, strong privacy controls, and seamless interoperability across institutions. Traditional EHR platforms depend heavily on centralized storage a infrastructure, which exposes sensitive medical information to security breaches, system failures, and limited patient oversight. These limitations also make compliance with data protection regulations, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), difficult to achieve. This research presents an interoperable EHR management framework built on a hybrid blockchain architecture that integrates Ethereum for transparent and immutable verification, Hyperledger Fabric for permissioned and institution-level control, and the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) for efficient decentralized storage of encrypted medical files. Smart contracts automate critical operations such as consent authorization, access auditing, and cryptographic key revocation to support GDPR-aligned data governance. The system is implemented through a Django backend and a React.js interface, enabling secure and intuitive interaction for patients and healthcare professionals. Experimental evaluation demonstrates reduced on-chain storage, improved access transparency, and stable transaction latency, confirming the suitability of the proposed framework for scalable and regulation-compliant healthcare data exchange.
References
[1] T. L. Tan, I. Salam and M. Singh, “Blockchain-based Healthcare Management System with Two-Side Verifiability,” PLOS ONE, Vol.17, No.4, pp.1–16, 2022.
[2] D. Tith, S. Y. Lee and S. W. Lee, “Application of Blockchain to Maintaining Patient Records in Electronic Health Records for Enhanced Privacy, Scalability and Availability,” Healthcare Informatics Research, Vol.26, No.3, pp.203–210, 2020.
[3] H. L. Wang et al., “Blockchain-Based Medical Record Management with Biofeedback Information,” in Smart Biofeedback: Perspectives and Applications, IntechOpen, pp.1–20, 2020.
[4] M. Usman, F. Qamar and A. Khalid, “Secure Electronic Medical Records Storage and Sharing using Blockchain Technology,” Procedia Computer Science, Vol.175, pp.369–375, 2020.
[5] A. Roehrs, C. A. Costa and R. da Rosa Righi, “OmniPHR: A Distributed Architecture Model to Integrate Personal Health Records,” Journal of Biomedical Informatics, Vol.71, pp.70–81, 2017.
[6] S. Zhang and J. Xue, “Security and Privacy on Blockchain,” ACM Computing Surveys, Vol.52, No.3, pp.1–34, 2019.
[7] A. Griggs, H. Ossher and R. Zhang, “Healthcare Data Sharing using Blockchain: Privacy and Scalability Challenges,” IEEE Access, Vol.9, pp.157651–157667, 2021.
[8] M. A. Khan and K. Salah, “IoT Security: Review, Blockchain Solutions, and Open Challenges,” Future Generation Computer Systems, Vol.82, pp.395–411, 2018.
[9] Y. Han, Y. Zhang and S. H. Vermund, “Blockchain Technology for Electronic Health Records,” International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, Vol.19, No.23, pp.1–22, 2022.
[10] H. S. A. Fang, T. H. Tan and Y. F. C. Tan, “Blockchain Personal Health Records: A Systematic Review,” Journal of Medical Internet Research, Vol.23, No.4, pp.1–14, 2021.
[11] T. Wang, X. Liu, Y. Zhang and H. Wang, “Health Data Security Sharing using Hybrid Blockchain Architecture,” Future Generation Computer Systems, Vol.154, pp.299–310, 2024.
[12] S. A. Hannan, “A Blockchain Technology to Secure Electronic Health Records in Healthcare System,” London Journal of Research in Computer Science and Technology, Vol.23, No.1, pp.1–13, 2023.
[13] N.Ettaloui, M.Bouzidi and A.Maach, “Blockchain-Based Electronic Health Records: A Systematic Review,” Health and Biomedical Engineering, Vol.2024, pp.1–12, 2024.
[14] C. Pradhan and A. Trehan, “Integration of Blockchain Technology in Secure Data Engineering Workflows,” International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.13, issue 1, pp.01–07, 2025.
[15] D. A. Oyemade and J. K. Oladele, “Secured Framework for Electronic Medical Record Protection and Exchange using Blockchain Technology,” International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.12, issue 5, pp.29–35, 2024.
[16] A. Azaria, A. Ekblaw, T. Vieira and A. Lippman, “MedRec: Using Blockchain for Medical Data Access and Permission Management,” in Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. on Open and Big Data, Vienna, pp.25–30, 2016.
[17] M. Mettler, “Blockchain Technology in Healthcare: The Revolution Starts Here,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on e-Health Networking, Munich, pp.1–3, 2016.
[18] G. S. Bhathal and U. S. Bhathal, “Quantum Safe Cryptography using Modern Hybrid Cryptography Techniques to Secure Data,” International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.13, Issue.4, pp.47–58, 2025.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




