FREQEnhanceNet: A Wavelet Transformer Hybrid for Low Light Enhancement
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v13i11.2128Keywords:
Low-light image enhancement, Wavelet transform, Vision transformer, Deep learning, Hybrid loss function, Convolutional neural networks, Frequency decomposition, Image denoisingAbstract
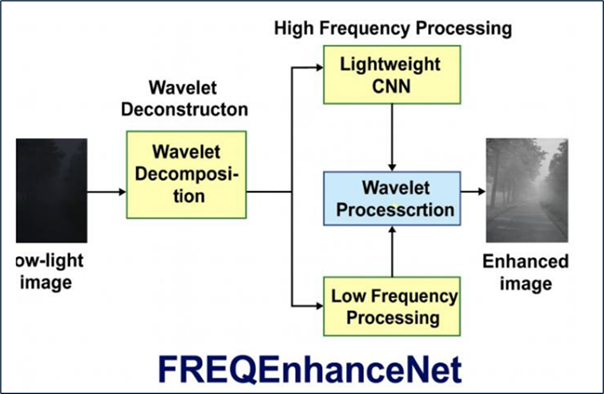
Low-light images often exhibit severe degradation, including amplified sensor noise, color distortion, and loss of fine details, which adversely affects perceptual quality and downstream computer vision tasks. To address these challenges, we propose FREQEnhanceNet, a hybrid neural architecture that integrates frequency-domain decomposition with transformer-based and convolutional processing. This design enables separate handling of broad illumination structure and fine-grained texture details. A two-dimensional discrete wavelet transform is applied to decompose the input into one low-frequency (LL) component representing global illumination and three high-frequency components capturing edges and textures. The LL component is processed by a vision transformer encoder-decoder that leverages self-attention to model long-range dependencies for global illumination correction. In parallel, the high-frequency components are refined by a lightweight convolutional module designed to denoise and sharpen local details. This specialized dual-path design allows each branch to address the distinct challenges of global adjustment and detail restoration. Training is guided by a novel frequency-aware hybrid loss that combines spatial reconstruction and perceptual objectives with an explicit frequency-domain term to encourage accurate texture recovery. Extensive experiments on the standard LOL-v1 and LOL-v2 low-light benchmarks demonstrate that FREQEnhanceNet achieves superior restoration quality. The proposed method consistently outperforms existing techniques in quantitative image quality metrics and yields visually more natural and detailed enhancements.
References
[1] S. Awasthi and S. W. A. Rizvi, “Proposed data sanitization for privacy preservation in mobile computing,” Cybernetics and Systems, Vol.55, No.7, pp.1729–1756, 2022, doi: 10.1080/01969722.2022.2145661.
[2] M. Afif, L. Jiao, and R. Hou, “Low-light image enhancement via multi-branch illumination estimation,” IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, Vol.26, pp.493–505, 2024.
[3] C. Liu, J. Liu, and S. Li, “Deep illumination prior: A transformer-based solution for night image enhancement,” IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, Vol.32, pp.1057–1069, 2023.
[4] H. Luo, Y. Zhang, and Z. Du, “Low-light image restoration via frequency-aware decomposition networks,” Neural Networks, Vol.168, pp.79–92, 2024.
[5] V. Singh and A. Bhardwaj, “Wavelet-assisted hybrid attention networks for image enhancement,” Pattern Recognition Letters, Vol.170, pp.87–95, 2023.
[6] T. Xu, R. Min, and F. Ma, “Edge-preserving transformer network for low-light image enhancement,” IEEE Access, Vol.11, pp.141221–141233, 2023.
[7] S. Jeon, Y. Park, and J. Yoon, “A dual-branch deep model for nighttime scene enhancement,” ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications (TOMM), Vol.20, No.3, pp.1–18, 2024.
[8] W. Zhang, L. Qiao, and K. Wang, “Multi-exposure learning for low-light image enhancement,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, Vol.34, No.5, pp.2245–2258, 2024.
[9] M. Zhai and Z. Lu, “Retinex-based deep wavelet network for enhanced night image quality,” Signal Processing, Vol.214, pp. 109441, 2023.
[10] H. Peng, Y. Wang, and X. Liu, “Masked transformer for illumination modeling in extremely dark images,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Computer Vision (ICCV), pp.2332–2341, 2023.
[11] G. Chen and L. Nie, “Illumination-guided frequency fusion network for low-light image enhancement,” Information Fusion, Vol.102, pp.102039, 2024.
[12] P. Khanna and Y. Kumar, “A CNN–transformer hybrid model for low-light image reconstruction,” Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, Vol.94, pp.104062, 2024.
[13] L. Guo and H. Tang, “Wavelet attention networks for image restoration tasks,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, Vol.35, No.2, pp.977–990, 2024.
[14] F. Rohani and M. Shah, “A comprehensive review of low-light image enhancement techniques,” ACM Computing Surveys, Vol.56, No.9, pp.1–36, 2023.
[15] J. Luo, H. Chen, and S. Wang, “Deep fusion Retinex model with transformer guidance,” IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, Vol.32, pp.6025–6038, 2023.
[16] D. Chang and M. Kim, “A multi-scale frequency aggregation network for efficient low-light enhancement,” Sensors, Vol.23, No.18, pp.7890, 2023.
[17] R. He and L. Xiao, “Noise-robust low-light enhancement via wavelet-domain denoising and illumination correction,” IEEE Sensors Journal, Vol.24, No.4, pp.6124–6135, 2024.
[18] A. Zhang, K. Huang, and S. Jin, “Dual-path transformer with frequency guidance for night photography enhancement,” IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, Vol.27, pp.512–523, 2024.
[19] N. Patel and R. Mehta, “Hybrid CNN–transformer model for adaptive image enhancement,” Pattern Analysis and Applications, Vol.27, No.2, pp.455–468, 2023.
[20] H. Lin, J. Wang, and Q. Zhao, “Low-light image recovery using multi-scale wavelet fusion,” Signal, Image and Video Processing, Vol.17, pp.445–458, 2023.
[21] Y. Sun and F. Wei, “Attention-guided image brightening network for dark scene restoration,” Applied Intelligence, Vol.53, pp.14233–14247, 2023.
[22] K. Roy and T. Ghosh, “Learning-based Retinex framework for night image enhancement,” Machine Vision and Applications, Vol.34, pp.88, 2023.
[23] M. Duarte and A. Silva, “Wavelet-driven deep enhancement for underexposed images,” Journal of Imaging, Vol.9, No.11, pp.215, 2023.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




