Automated Cancer Detection in Human Blood Samples of Microscopic Images Using Machine Learning Techniques for Enhanced Diagnosis and Classification
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v13i10.913Keywords:
Cancer Detection, Microscopic Images, Machine Learning, MATLAB, Blood Sample Classification, Computer-Aided DiagnosisAbstract
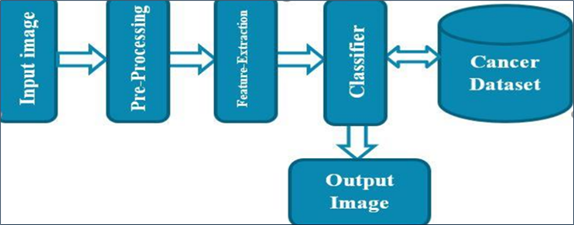
Cancer remains one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, with early detection being critical for improving patient survival rates. Manual microscopic examination of blood samples is time-consuming, subjective, and requires significant expertise, which often leads to diagnostic delays and misinterpretations. In this study, we propose an automated cancer detection framework using microscopic blood smear images analyzed with machine learning techniques in MATLAB. The proposed methodology consists of three major phases: preprocessing and enhancement of blood images, feature extraction using morphological and texture-based descriptors, and classification using machine learning models. The results demonstrate that the system can effectively differentiate cancerous blood samples from normal samples with high accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and specificity. Comparative analysis with existing approaches highlights the superior performance of our system, particularly in terms of robustness and diagnostic reliability. This research contributes to the growing body of computer-aided diagnosis systems and provides a foundation for future improvements in automated cancer diagnostics.
References
[1] R. Suriyagrace and M. Devapriya, “Effective Image Pre-Processing Techniques with Deep Learning for Leukemia Detection,” International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering (IJCSE), Vol.9, Issue.10, pp.28–36, 2021.
[2] Afsheen Firdous, Kompella Venkata Ramana, “A Study on Lymphoblastic Leukemia Using Image Processing,” International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering (IJCSE), Vol.8, Issue.10, pp.147–157, 2020.
[3] A. B. Chate and S. N. Holambe, “Adaptive approach for detection and localization of iris features for authentication using digital image processing techniques,” International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications in Engineering, Vol.12, No.4s, pp.82–87, 2023.
[4] A. Chate and S. Holambe, “Classification of iris image features using supervised and unsupervised learning,” in Information and Communication Technology for Competitive Strategies (ICTCS), Singapore: Springer, 2023.
[5] Y. M. Kobara, I. J. Akpan, A. D. Nam, F. H. AlMukthar, and M. Peter, “Artificial intelligence and data science methods for automatic detection of white blood cells in images,” Journal of Imaging Informatics in Medicine, Vol.6, No.1, pp.1–10, 2025.
[6] T. M. Makki and K. A. Dulaimi, “Blood cell microscopic image classification in computer-aided diagnosis using machine learning: A review,” Iraqi Journal for Computer Science and Mathematics, Vol.4, No.2, pp.1–15, 2023.
[7] L. Schwartz, “A blood test-based machine learning model for predicting lung cancer,” Journal of Clinical Oncology, Vol.43, No.14, pp.1234–1242, 2025.
[8] S. Rashid, M. Raza, M. Sharif, F. Azam, and S. Kadry, “White blood cell image analysis for infection detection based on virtual hexagonal trellis using deep learning,” Scientific Reports, Vol.13, No.1, pp.17827, 2023.
[9] J. Musigmann, “Use of automated machine learning in cancer diagnostics,” Diagnostics, Vol.13, No.14, pp.2315, 2023.
[10] G. M. Karageorgos et al., “Deep learning-based automated pipeline for blood vessel detection and distribution analysis in multiplexed prostate cancer images,” Frontiers in Bioinformatics, Vol.14, pp.1296667, 2023.
[11] L. Kumar, “Automating cancer diagnosis using advanced deep learning models,” Scientific Reports, Vol.14, pp.75876, 2024.
[12] A. Shehta, “Blood cancer prediction model based on deep learning techniques,” Scientific Reports, Vol.14, pp.84475, 2024.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




