A Predictive Framework for Hourly Wind Speed Forecasting Using Stacked Recurrent Neural Networks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v13i10.18Keywords:
Wind speed forecasting, Deep learning, recurrent neural networks, Gated Recurrent Unit, Long Short-Term Memory Networks, Mean Absolute errorAbstract
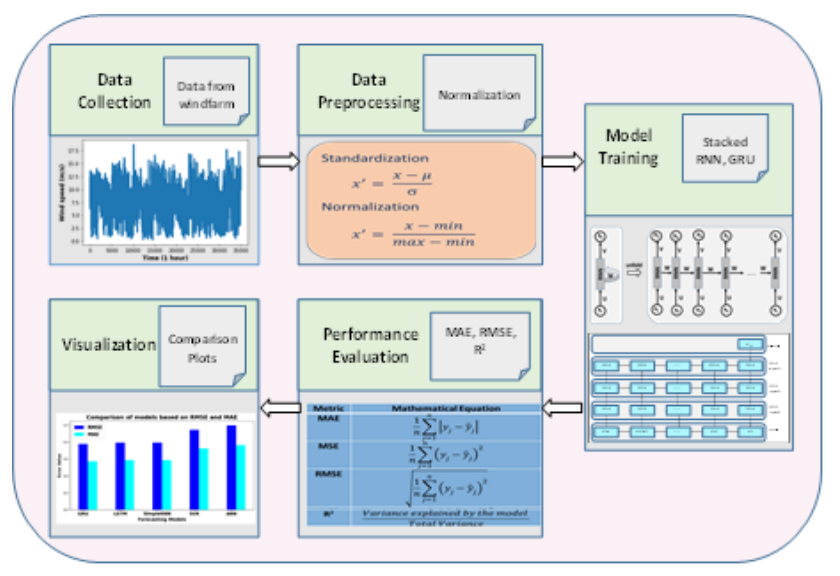
The growing demand for low-cost, eco-friendly energy has established wind power as a pivotal renewable source, making accurate wind speed forecasting critical. The study introduces a deep learning framework that integrates stacked Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks to predict hourly wind speed. The model’s performance is assessed using Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), and the Coefficient of Determination (R²), and benchmarked against Support Vector Regression (SVR) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) models. Experimental findings reveal that the proposed stacked GRU and LSTM models consistently surpass the comparative methods, highlighting its robustness and effectiveness in wind speed forecasting.
References
[1] Zhang, D., Peng, X., Pan, K. and Liu, Y., “A novel wind speed forecasting based on hybrid decomposition and online sequential outlier robust extreme learning machine”. Energy conversion and management, 180, pp.338-357, 2019.
[2] Liu, H., Chen, C., Lv, X., Wu, X. and Liu, M., 2019. Deterministic wind energy forecasting: A review of intelligent predictors and auxiliary methods. Energy Conversion and Management, 195, pp.328-345, 2019.
[3] Jaseena, K.U. and Kovoor, B.C., “A hybrid wind speed forecasting model using stacked autoencoder and LSTM”. Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, Vol.12, Issue.2, pp.023302, 2020.
[4] Liu, Z., Jiang, P., Zhang, L. and Niu, X., “A combined forecasting model for time series: Application to short-term wind speed forecasting”. Applied Energy, 259, pp.114137, 2020.
[5] Wu, Y.X., Wu, Q.B. and Zhu, J.Q”Data?driven wind speed forecasting using deep feature extraction and LSTM”. IET Renewable Power Generation, Vol.13, Issue.12, pp.2062-2069, 2019.
[6] Wu, Y.X., Wu, Q.B. and Zhu, J.Q. “Data?driven wind speed forecasting using deep feature extraction and LSTM”. IET Renewable Power Generation, Vol.13, Issue.12, pp.2062-2069, 2019.
[7] Qolipour, M., Mostafaeipour, A., Saidi-Mehrabad, M. and Arabnia, H.R., “Prediction of wind speed using a new Grey-extreme learning machine hybrid algorithm: A case study”. Energy & Environment, Vol.30, Issue.1, pp.44-62, 2019.
[8] Kavasseri, R.G. and Seetharaman, K., Day-ahead wind speed forecasting using f-ARIMA models. Renewable Energy, Vol.34, Issue.5, pp.1388-1393, 2009.
[9] Liu, M., Cao, Z., Zhang, J., Wang, L., Huang, C. and Luo, X., “ Short-term wind speed forecasting based on the Jaya-SVM model. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 121, pp.106056, 2020.
[10] Neshat, M., Nezhad, M.M., Abbasnejad, E., Mirjalili, S., Tjernberg, L.B., Garcia, D.A., Alexander, B. and Wagner, M “A deep learning-based evolutionary model for short-term wind speed forecasting: A case study of the Lillgrund offshore wind farm”. Energy Conversion and Management, 236, pp.114002, 2021.
[11] Wang, Y., Xu, H., Zou, R., Zhang, F. and Hu, Q., “Dynamic non-constraint ensemble model for probabilistic wind power and wind speed forecasting”. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 204, pp.114781, 2024.
[12] Hao, Y., Wang, X., Wang, J. and Yang, W., “A new perspective of wind speed forecasting: Multi-objective and model selection-based ensemble interval-valued wind speed forecasting system”. Energy Conversion and Management, 299, pp.117868, 2024.
[13] Du, P., Yang, D., Li, Y. and Wang, J., “An innovative interpretable combined learning model for wind speed forecasting”. Applied Energy, 358, pp.122553, 2024.
[14] Wu, B., Yu, S., Peng, L. and Wang, L., “Interpretable wind speed forecasting with meteorological feature exploring and two-stage decomposition”. Energy, 294, pp.130782, 2024.
[15] Parri, S. and Teeparthi, K., “VMD-SCINet: a hybrid model for improved wind speed forecasting”. Earth Science Informatics, Vol.17, Issue.1, pp.329-350, 2024.
[16] Li, Y., Sun, K., Yao, Q. and Wang, L., “A dual-optimization wind speed forecasting model based on deep learning and improved dung beetle optimization algorithm”. Energy, 286, pp.129604, 2024.
[17] Nielsen, M. A. “Neural networks and deep learning”. San Francisco, CA, USA, Determination press publisher, Vol.25, 2015.
[18] Hochreiter, S., and Schmidhuber, J. “Long short-term memory”. Neural computation, Vol.9, Issue.8, pp.1735-1780, 1997.
[19] Jaseena K U and Binsu C Kovoor. “Deep learning based multi-step short term wind speed forecasts with LSTM”. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Data Science, E-Learning and Information Systems (DATA `19). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 7, pp.1–6, 2019.
[20] Jaseena, K.U. and Kovoor, B.C., “Deterministic weather forecasting models based on intelligent predictors: A survey”. Journal of king saud university-computer and information sciences, Vol.34, Issue.6, pp.3393-3412, 2022.
[21] Jaseena, K.U. and Kovoor, B.C.,“A Wavelet-based hybrid multi-step Wind Speed Forecasting model using LSTM and SVR”. Wind Engineering, Vol.45, Issue.5, pp.1123-1144, 2021.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




