Neural Networks in Multimodal Emotion Recognition: A Comprehensive Survey of Models, Fusion, and Data
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v13i9.3141Keywords:
Neural Networks,, Emotion Recognition,, Convolutional Neural Networks,, Multimodal Fusion, Sentiment Analysis,, Human-Computer InteractionAbstract
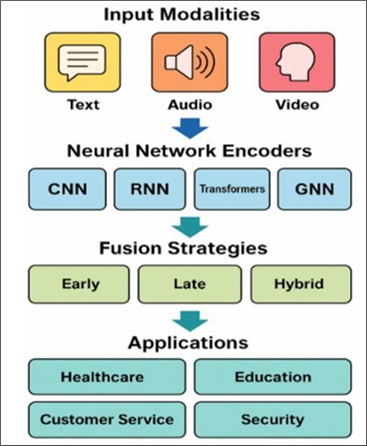
Emotion recognition is a pivotal element in building systems that understand and respond to human affect. As single- modal approaches often struggle with ambiguity and environmental variability, multimodal emotion recognition has emerged as a more robust alternative by integrating cues from facial expressions, voice, and text. However, despite its growing importance, the literature still lacks a comprehensive and focused review that brings together current advancements, challenges, and practical insights specific to multimodal emotion recognition—this gap motivates our work. This survey explores recent progress in the field, highlighting how neural networks support multimodal integration by learning complex patterns across different data types. First, we identify a set of essential criteria that a sound emotion recognition system should satisfy—such as accuracy, adaptability, real-time capability, and interpretability and use them to frame our evaluation of existing methods. While neural networks like CNNs, RNNs, and Transformers are key enablers, our emphasis is on their application within multimodal systems rather than detailed architectural analysis. We review various fusion strategies for combining modalities, examine their strengths and limitations, and discuss common challenges that include synchronization issues, limited data availability, computational demands, and fairness concerns. By synthesizing current research and outlining future directions, this survey aims to provide a comprehensive yet focused overview of multimodal emotion recognition, emphasizing the supportive but crucial role of neural networks in improving performance and real-world applicability.
References
[1] S. Tripathi and J. Beigi, “Multi-modal emotion recognition on IEMOCAP dataset using deep learning,” in Proc. Interspeech, 2018.
[2] A. Mollahosseini, D. Chan, and M. H. Mahoor, “Going deeper in facial expression recognition using deep neural networks,” in Proc. IEEE WACV, 2016.
[3] Z. Lian, Y. Chen, M. Xu, et al., “DER-GCN: Dialog and event relation-awareGCNforemotionrecognition,” IEEE/ACMTrans. Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2023.
[4] Z. Lian, Y. Chen, M. Xu, et al., “PIRNet: Personality-enhanced iterative refinement network for emotion recognition in conversation,” IEEE Trans. Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024.
[5] M. Soleymani, S. Asghari-Esfeden, Y. Fu, and M. Pantic, “Analysis of EEG signals and facial expressions for emotion detection,” IEEE Trans. Affective Computing, 2016.
[6] A. Zadeh, P. P. Chan, S. Pu, et al., “CMU-MOSEI: A multimodal language dataset,” in Proc. ACL, 2018.
[7] A. Zadeh, M. Chen, S. Poria, E. Cambria, and L.-P. Morency, “Multimodal sentiment analysis using hierarchical fusion with context modeling,” in Proc. ACL, 2018.
[8] Y. Kim and E. M. Provost, “Emotion classification via GRUs with attention for speech,” in Proc. IEEE ICASSP, 2017.
[9] C. Busso, M. Bulut, C.-C. Lee, et al., “IEMOCAP: Interactive emotional dyadic motion capture database,” Language Resources and Evaluation, Vol.42, No.4, pp.335–359, 2008.
[10] T. Baltrusaitis, C. Ahuja, and L.-P. Morency, “Multimodal? machine learning: A survey and taxonomy,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol.41, No.2, pp.423–443, 2019.
[11] P. Ekman and W. V. Friesen, Facial Action Coding System: A Technique for the Measurement of Facial Movement. Consulting Psychologists Press, 1978.
[12] C. Wu, C.-H. Wu, and Y. Tsao, “Speech emotion recognition using CNN with audio word embeddings,” in Proc. Interspeech, 2018.
[13] A. Azarian and S. Narayanan, “Cross-modal attention for multimodal emotion recognition,” in Proc. IEEE ICASSP, 2020.
[14] J. Zhao, Y. Miao, Y. Liu, et al., “Understanding dataset bias in multimodal emotion recognition,” in Proc. NeurIPS, 2022.
[15] A. Batliner, S. Steidl, B. Schuller, et al., “The automatic recognition of emotions in speech: Problems and opportunities,” in Emotion-Oriented Systems: The Humaine Handbook, Springer, pp.111–135, 2011.
[16] S. Huang, W. Gao, and Q. Xuan, “Audio–visual emotion recognition using deep cross-modal fusion,” IEEE Trans. Multimedia, 2019.
[17] C. Wang, X. Zhang, and Z. Zhu, “Transformer-based multimodal emotion recognition,” in Proc. IEEE ICASSP, 2021.
[18] N. Tzirakis, G. Trigeorgis, M. A. Nicolaou, B. W. Schuller, and S. Zafeiriou, “End-to-end multimodal emotion recognition using deep neural networks,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, Vol.39, No.1, pp.99–114, 2021.
[19] L. Shen, J. Zhang, and Y. Chen, “Privacy-preserving federated learning for emotion recognition,” in Proc. IEEE PerCom, 2021.
[20] H. Yang, Z. Zhang, and J. Cao, “Fairness-aware multimodal emotion recognition,” in Proc. IEEE FG, 2022.
[21] H. Lian, “A Survey of Deep Learning-Based Multimodal Emotion Recognition: Speech, Text, and Face,” Entropy, Vol.25, No.10, pp.1440, 2023.
[22] N. Ahmed, Z. Al Aghbari, and S. Girija, “A systematic survey on multimodal emotion recognition using learning algorithms,” Intelligent Systems with Applications, Vol.17, pp.200108, 2023.
[23] M. P. A. Ramaswamy, “Multimodal emotion recognition: A comprehensive review,” WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, Vol.14, No.2, pp.e1563, 2024.
[24] C. Wu, Y. Cai, Y. Liu, P. Zhu, Y. Xue, Z. Gong, and B. Ma, “Multimodal Emotion Recognition in Conversations: A Survey of Methods, Trends, Challenges and Prospects,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.20511, 2025.
[25] K. Devarajan, “Enhancing Emotion Recognition Through Multi-Modal Data with GNN Feature Fusion,” Intelligent Systems with Applications, Vol.20, pp.200095, 2025.
[26] Y. Wu, S. Zhang, and P. Li, “Multi-modal emotion recognition in conversation based on prompt learning with text-audio fusion features,” Scientific Reports, Vol.15, No.1, pp.89758, 2025.
[27] A. A. Wafa, M. M. Eldefrawi, and M. S. Farhan, “Advancing multimodal emotion recognition in big data through prompt engineering and deep adaptive learning,” Journal of Big Data, Vol.12, No.1, pp.164, 2025.
[28] P. Sarala, S. O. Sadjadi, D. Manocha, and R. D. Sriram, “Multimodal emotion recognition using transfer learning from speaker recognition and BERT-based models,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.08974, 2022.
[29] D. Hu, X. Hou, L. Wei, L. Jiang, and Y. Mo, “MM-DFN: Multimodal Dynamic Fusion Network for Emotion Recognition in Conversations,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.02385, 2022.
[30] Q. Wei, X. Huang, and Y. Zhang, “FV2ES: A Fully End-to-End Multimodal System for Fast Yet Effective Video Emotion Recognition Inference,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.10170, 2022.
[31] G. Hu, T. Lin, Y. Zhao, G. Lu, Y. Wu, and Y. Li, “UniMSE: Towards Unified Multimodal Sentiment Analysis and Emotion Recognition,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.11256, 2022.
[32] D. Li, H. Wang, Y. Zhu, and S. Chen, “Joyful: Joint Modality Fusion and Graph Contrastive Learning for Multimodal Emotion Recognition,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.11009, 2023.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




