CCTV Surveillance Systems and Their Impact on Traffic Compliance and Public Road Behavior in Goa
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v13i9.2330Keywords:
Traffic Behavior, CCTV SurveillanceAbstract
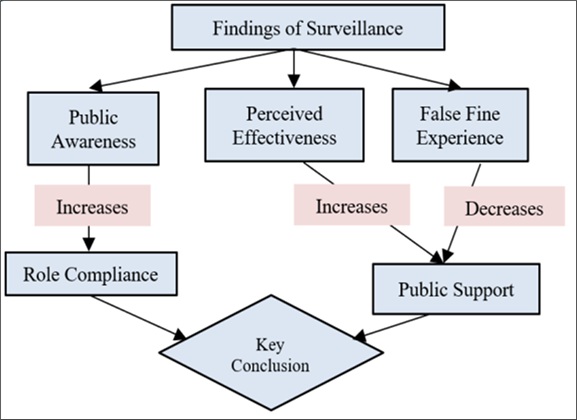
Traffic violations are a major cause of accidents and reduced traffic safety in Goa. CCTV cameras can enhance monitoring and enforcement. This study examines the link between public awareness, perceptions, and experiences with CCTV surveillance, and how these factors influence actual traffic behavior and support for further expansion. Data were collected through a structured public survey capturing demographic information, driving behaviors, and opinions on CCTV. Three hypotheses were tested using the chi-square test of independence: (1) the relationship between awareness of CCTV and rule compliance, (2) the relationship between perceived effectiveness of CCTV and support for expansion, and (3) the relationship between experiences of false fines and support for expansion. All hypotheses showed statistically significant relationships. Findings indicate that greater public awareness and belief in CCTV effectiveness led to higher compliance and stronger support for deployment. Conversely, negative experiences, such as false fines, reduce public support. The study concludes that public awareness campaigns, system accuracy, and concerns about privacy must be addressed to ensure successful CCTV implementation.
References
[1] R. Kaur and P. Singh, “Public Trust and Transparency in AI-Based Traffic Management Systems,” International Journal of Smart Cities, Vol.7, No.1, pp.22-40, 2023.
[2] J. Smith and A. Doe, “The deterrent effect of CCTV on traffic violations,” Journal of Urban Safety, Vol.10, No.2, pp.45-59, 2021.
[3] L. Zhang, G. P. Hancke, K. Huang, and E. Nurellari, “Public acceptance of intelligent transportation systems: A review,” Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, Vol.135, pp.103512, 2022.
[4] L. Abramson and B. Miller, “The Cost of Error: How False Fines Erode Trust in Automated Law Enforcement,” Ethics and Information Technology, Vol.22, No.3, pp.253-262, 2020.
[5] K. Brown and P. Green, “Privacy Versus Security: A Study of Public Attitudes towards Traffic Surveillance Technologies,” Surveillance & Society, Vol.19, No.4, pp.456-471, 2021.
[6] A. Prajapati, R. Pugalia, K. Patil, and Pradeepkumar, “CCTV Based Traffic Control System,” International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology, Vol.5, No.1, 2017.
[7] S. Patel and J. Lee, “Cybersecurity Risk Assessment in IoT-Based Public Infrastructure: A Case Study of Traffic Surveillance Networks,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, Vol.210, pp.103539, 2023.
[8] M. Johnson, “Automated enforcement and procedural fairness: The challenge of the false positive,” Law & Technology Review, Vol.18, pp.112-130, 2020.
[9] X. Chen and Y. Wang, “Efficacy of Camera-Based Enforcement on Motorcycle Helmet Compliance: A Comparative Analysis,” Accident Analysis & Prevention, Vol.144, pp.105599, 2020.
[10] P. Kumar and S. Sharma, “An IoT-based Smart Traffic Management System using Computer Vision,” International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.11, No.5, pp.10-15, 2023.
[11] F. Garcia, M. Martinez, and R. Lopez, “Demographic Determinants of Public Perception on Urban Surveillance,” Computers in Human Behavior, Vol.127, pp.107042, 2022.
[12] N. Davis, “Ethical Guidelines for Public Area Surveillance in the Age of AI,” Science and Engineering Ethics, Vol.28, No.3, pp.21, 2022.
[13] H. Kim and J. Park, “A Cost-Benefit Analysis Model for the Implementation of CCTV Traffic Enforcement Systems,” Sustainable Cities and Society, Vol.75, pp.103291, 2021.
[14] M. L. McHugh, “The chi-square test of independence,” Biochemia Medica, Vol.23, No.2, pp.143-149, 2013.
[15] Q. Su et al., “Camera Planning for Physical Safety of Outdoor Electronic Devices: Perspective and Analysis,” IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, Vol.12, No.8, pp.1530-1543, 2025.
[16] T. White and L. Evans, “Public Perception of AI in Urban Surveillance: A Meta-Analysis,” Technology in Society, Vol.74, pp.102312, 2023.
[17] A. Gupta and R. Mehta, “A Review of Statistical Methods in Social Science Research,” International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.10, No.4, pp.25-30, 2022.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




