Transfer Learning Approach Using ImageNet CNN for Diabetic Retinopathy Detection and Classification from Fundus Images
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v13i9.17Keywords:
Transfer Learning, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)Abstract
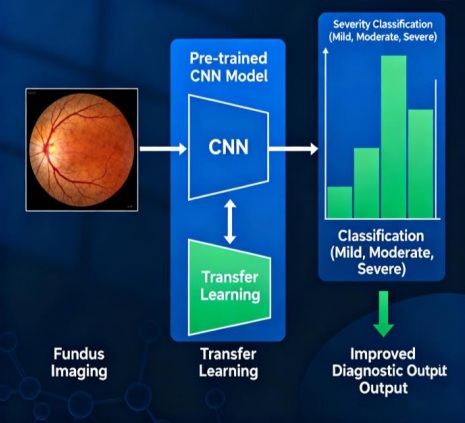
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is one of the leading causes of preventable blindness worldwide, and its early detection plays a vital role in reducing vision impairment. Recent advances in deep learning have demonstrated significant potential in automating the screening and classification of retinal diseases. This paper presents a transfer learning-based approach for the detection and classification of DR from fundus images using a pre-trained Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model trained on the ImageNet dataset. By fine-tuning the network with a large-scale fundus image dataset, the proposed method effectively leverages learned visual representations to capture intricate retinal features. The experimental results indicate high accuracy in distinguishing between different severity levels of DR, outperforming conventional machine learning techniques. The findings highlight that transfer learning not only reduces training time but also enhances model generalization, making it a reliable tool for computer-aided diagnosis in ophthalmology.
References
[1] X. Li, T. Pang, “CNN Transfer Learning for Fundus Images,” In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Imaging, pp.1-5, 2017.
[2] C. Lam, et al., “Automated Diabetic Retinopathy Detection using Convolutional Neural Networks,” IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, Vol.37, Issue.12, pp.1-10, 2018.
[3] I. Kandel, et al., “CNN Transfer Learning for Diabetic Retinopathy Classification: A Review,” Journal of Medical Systems, Vol.44, Issue.5, pp.1-12, 2020.
[4] D. Le, et al., “Transfer Learning for OCTA Diabetic Retinopathy Detection,” Computers in Biology and Medicine, Vol.120, Issue.2, pp.1-9, 2020.
[5] W.L. Alyoubi, et al., “Deep Learning for Diabetic Retinopathy Detection: A Comprehensive Review,” Healthcare Informatics Research, Vol.26, Issue.4, pp.1-8, 2020.
[6] I. Kandel, et al., “CNN Transfer Learning Approaches for Diabetic Retinopathy Classification,” Pattern Recognition Letters, Vol.135, Issue.7, pp.1-7, 2020.
[7] M.K. Jabbar, et al., “Transfer Learning-Based Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis using EyePACS Dataset,” International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, Vol.32, Issue.4, pp.1-10, 2022.
[8] M.K. Jabbar, et al., “Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis using Retinal Images and Transfer Learning,” Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, Vol.13, Issue.6, pp.1-12, 2022.
[9] M.M. Butt, et al., “Hybrid Deep Learning for Diabetic Retinopathy Detection,” Computers in Biology and Medicine, Vol.143, pp.1-9, 2022.
[10] M.M. Butt, et al., “Hybrid CNN Feature Extraction for Improved Diabetic Retinopathy Detection,” Expert Systems with Applications, Vol.190, pp.1-10, 2022.
[11] B. Oltu, et al., “Systematic Review: Transfer Learning for Diabetic Retinopathy Detection,” IEEE Access, Vol.11, pp.1-12, 2023.
[12] M.S.H. Talukder, et al., “Improved Diabetic Retinopathy Detection using Transfer Learning,” Multimedia Tools and Applications, Vol.82, Issue.14, pp.1-15, 2023.
[13] L. Arora, et al., “Ensemble Deep Learning and EfficientNet for Diabetic Retinopathy Classification,” Sensors, Vol.24, Issue.3, pp.1-12, 2024.
[14] L. Arora, et al., “EfficientNet Ensemble Approaches for Robust Diabetic Retinopathy Classification,” Applied Sciences, Vol.14, Issue.4, pp.1-12, 2024.
[15] S. Vallukappully, et al., “Early Diabetic Retinopathy Detection using NASNet-Large,” Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, Vol.91, pp.1-9, 2025.
[16] S. Vallukappully, et al., “High-Accuracy Diabetic Retinopathy Classification using NASNet-Large,” IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, Vol.29, Issue.1, pp.1-10, 2025.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




