Automatic Modulation Classification using a Deep Learning model based on ResNet
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v13i8.110Keywords:
Automated Modulation Classification (AMC), ), Deep Learning (DL),, ResNet-Model, CNN, Signal Classification, Cognitive Radio Networks,, Adversarial ConditionsAbstract
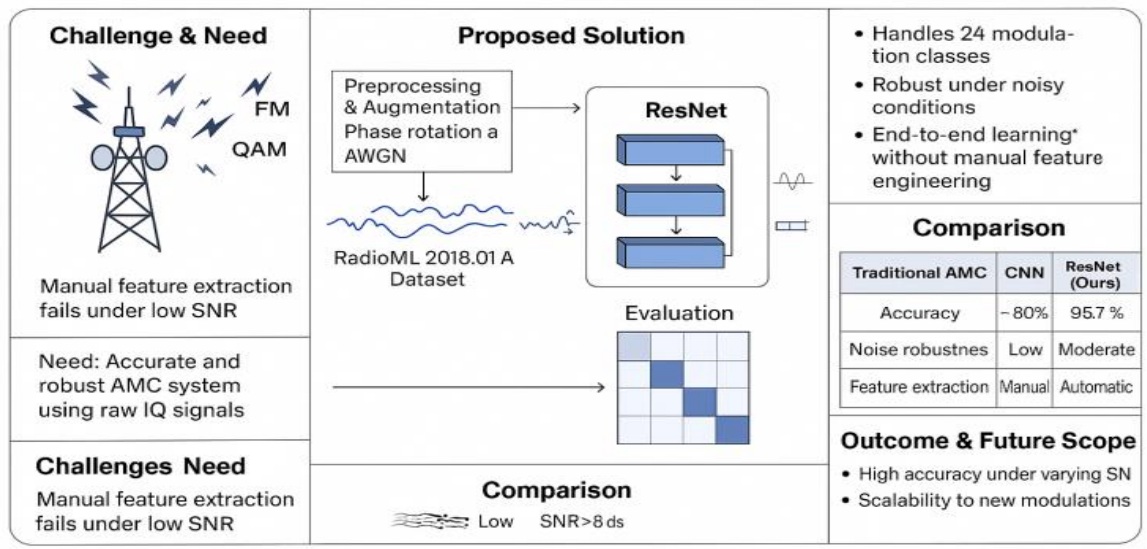
Automatic Modulation Classification (AMC) serves as a foundational element in contemporary wireless communication systems, enabling adaptive signal processing and efficient spectrum management. This study explores deep learning-based approaches—particularly a Res-Net architecture—for robust AMC performance using the benchmark RADIOML 2018.01A dataset. The dataset comprises 24 modulation schemes across a wide SNR range from -20 dB to +30 dB. Comprehensive data preprocessing was performed, including normalization, as well as various augmentation methods like phase rotation, temporal shifting, and artificial noise addition to strengthen the model’s resilience and ability to generalize under challenging conditions. A Res-Net model was constructed and optimized with categorical cross-entropy as the loss function and Adam as the learning algorithm. The model achieved a test accuracy of 95.72% under high-SNR conditions (SNR > 8 dB) with a low training loss of 0.0933, demonstrating strong convergence and generalization capabilities. Confusion matrix analysis highlighted the model’s strengths in accurately classifying most modulation types, while revealing challenges in differentiating between similar schemes like 16QAM and 64QAM under low SNR conditions. The findings confirm that the proposed deep learning framework is capable of learning and distinguishing complex signal characteristics directly from unprocessed I/Q data without the need for manual feature crafting. Future work will focus on integrating Transformer-based architectures, wavelet transform features, and hybrid CNN–RNN models to improve performance in noisy environments. The results underscore the potential of deep learning for deploying AMC in cognitive radio, signal surveillance, and secure communication systems.
References
[1] Wu, Z., Zhou, S., Yin, Z., Ma, B., & Yang, Z., “Robust automatic modulation classification under varying noise conditions”, IEEE Access, Vol.5, pp.19733-19741, 2017.
[2] Abdel?Moneim, M.A., El?Shafai, W., Abdel?Salam, N., El?Rabaie, E.S.M., & Abd El?Samie, F.E., “A survey of traditional and advanced automatic modulation classification techniques, challenges, and some novel trends”, International Journal of Communication Systems, Vol.34, No.10, pp.e4762, 2021.
[3] Dekker, E., Tanis, P.J., Vleugels, J.L., Kasi, P.M., & Wallace, M., “Pure-amc”, Lancet, Vol.394, pp.1467-1480, 2019.
[4] Yin, H., & Diao, J., “Signal automatic modulation based on AMC neural network fusion”, PLOS One, Vol.19, No.6, pp.e0304531, 2024.
[5] Zhao, Y., Deng, T., Gavin, B., Ball, E.A., & Seed, L., “An Ultra-low Cost and Accurate AMC Algorithm and its Hardware Implementation”, IEEE Open Journal of the Computer Society, 2024.
[6] Singh, V., Khodadadi, M., Khalily, M., Tafazolli, R., & Kishk, A.A., “AMC-Based Miniaturized Waveguide With Reconfigurable Pass-Bands Below Cut-Off Frequency and Quasi-TEM Mode”, IEEE Open Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2024.
[7] Kim, J., Lee, K.J., Sung, C.K., & Lee, I., “A simple SNR representation method for AMC schemes of MIMO systems with ML detector”, IEEE Transactions on Communications, Vol.57, No.10, pp.2971-2976, 2009.
[8] Pajic, M.S., Veinovic, M., Peric, M., & Orlic, V.D., “Modulation order reduction method for improving the performance of AMC algorithm based on sixth–order cumulants”, IEEE Access, Vol.8, pp.106386-106394, 2020.
[9] Li, Z., Wang, Q., Liu, W., Xu, Q., Xing, Z., & Li, Y., “Practical AMC model based on SAE with various optimisation methods under different noise environments”, IET Communications, Vol.14, No.22, pp.4081-4088, 2020.
[10] Chen, L.S., Chung, W.H., Chen, Y., & Kuo, S.Y., “AMC with a BP-ANN scheme for 5G enhanced mobile broadband”, IEEE Access, 2020.
[11] Makowski, D., Piotrowski, A., & Napieralski, A., “Universal communication module based on AMC standard”, In Proceedings of the 2008 15th International Conference on Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, IEEE, June, pp.139-143, 2008.
[12] Nesraoui, O., Teguig, D., & Sadoudi, S., “SDR implementation of a light deep learning model based CNN for joint spectrum sensing and AMC”, Physica Scripta, Vol.99, No.5, pp.056008, 2024.
[13] Meng, F., Chen, P., Wu, L., & Wang, X., “Automatic modulation classification: A deep learning enabled approach”, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, Vol.67, No.11, pp.10760-10772, 2018.
[14] Song, S., Chandrasekhar, V., Mandal, B., Li, L., Lim, J.H., Sateesh Babu, G., et al., “Multimodal multi-stream deep learning for egocentric activity recognition”, In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp.24-31, 2016.
[15] Concha, D.T., Maia, H.D.A., Pedrini, H., Tacon, H., Brito, A.D.S., Chaves, H.D.L., & Vieira, M.B., “Multi-stream convolutional neural networks for action recognition in video sequences based on adaptive visual rhythms”, In Proceedings of the 2018 17th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), IEEE, December, pp.473-480, 2018.
[16] Perveen, G., Ali, S.F., Ahmad, J., Shahab, S., Adnan, M., Anjum, M., & Khosa, I., “Multi-Stream Deep Convolution Neural Network With Ensemble Learning for Facial Micro-Expression Recognition”, IEEE Access, 2023.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




