Improving Classification Performance in Brain Tumor Based on Convolutional Neural Networks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v13i7.1017Keywords:
CNN, Brain Tumor Classification,, Deep Learning, Grad-CAMAbstract
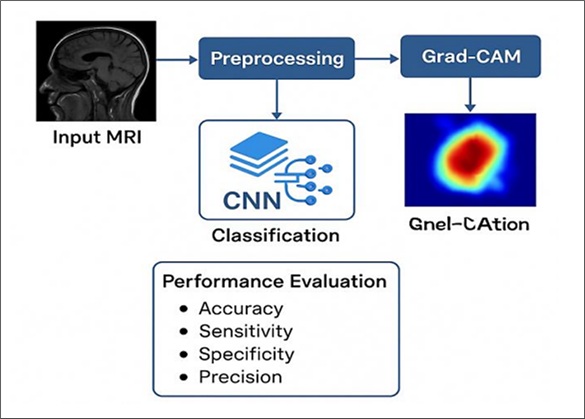
Accurately identifying brain tumors plays a vital role in early diagnosis and the development of appropriate treatment strategies. Traditional interpretation of MRI scans by radiologists can be time-consuming and subject to variability. This study proposes an automated classification framework based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to improve diagnostic consistency and speed. Utilizing a dataset comprising 3,060 MRI images, the model leverages the Grad-CAM technique to visualize key regions influencing its decisions. Rigorous testing was carried out, measuring performance through metrics including accuracy, precision, recall, and specificity. Results demonstrate that the CNN-driven model offers superior classification performance and enhanced transparency when compared to conventional methods. This work contributes to advancing intelligent diagnostic systems and serves as a valuable tool for medical professionals seeking more dependable and rapid evaluations.
References
[1] L. Kapoor and S. Thakur, “A survey on brain tumor detection using image processing techniques”, 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science Engineering - Confluence, pp.582–585, 2017. DOI: 10.1109/CONFLUENCE.2017.7943218.
[2] S. K. Singh et al., “Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors”, Cancer Research, Vol.63, No.18, pp.5821–5828, 2003.
[3] M. U. Akram and A. Usman, “Computer aided system for brain tumor detection and segmentation”, in International Conference on Computer Networks and Information Technology, pp.299–302, 2011.
[4] A. M. Alqudah et al., “Brain tumor classification using deep learning technique–a comparison between cropped, uncropped, and segmented lesion images with different sizes”, arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.08844, 2020.
[5] A. Veeramuthu et al., “MRI brain tumor image classification using a combined feature and image-based classifier”, Frontiers in Psychology, Vol.13, 2022.
[6] H. Kibriya et al., “A novel and effective brain tumor classification model using deep feature fusion and famous machine learning classifiers”, Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2022.
[7] S. A. Nawaz et al., “Brain tumor classification based on hybrid optimized multi-features analysis using magnetic resonance imaging dataset”, Applied Artificial Intelligence, pp.1–27, 2022.
[8] S. Deepak and P. Ameer, “Brain tumor classification using deep CNN features via transfer learning”, Computers in Biology and Medicine, Vol.111, pp.103-345, 2019.
[9] X. Gu et al., “Brain tumor MR image classification using convolutional dictionary learning with local constraint”, Frontiers in Neuroscience, Vol.15, pp.679-847, 2021.
[10] Analytics Vidhya, “Image classification with TensorFlow: Data augmentation on streaming data – part 2”, 2021.
[11] S. S. Basha et al., “Impact of fully connected layers on performance of convolutional neural networks for image classification”, Neurocomputing, Vol.378, pp.112–119, 2020.
[12] Ahmed Hamada, “Brain tumor detection dataset”, Kaggle. 2022.
[13] N. M. Dipu et al., “Brain tumor detection using various deep learning algorithms”, International Conference on Science & Contemporary Technologies (ICSCT), pp.1–6, 2021.
[14] S. Albawi et al., “Understanding of a convolutional neural network”, in 2017 International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICET), pp.1–6, 2017. DOI: 10.1109/ICEngTechnol.2017.8308186.
[15] G. Yao et al., “A review of convolutional-neural-network-based action recognition”, Pattern Recognition Letters, Vol.118, pp.14–22, 2019.
[16] T. Kattenborn et al., “Review on convolutional neural networks (CNN) in vegetation remote sensing”, ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Vol.173, pp.24–49, 2021.
[17] W. Fang et al., “Computer vision for behaviour-based safety in construction: A review and future directions”, Advanced Engineering Informatics, Vol.43, 100980, 2020.
[18] D. Palaz et al., “End-to-end acoustic modeling using convolutional neural networks for HMM-based automatic speech recognition”, Speech Communication, Vol.108, pp.15–32, 2019.
[19] H.-C. Li et al., “Lightweight and resource-constrained learning network for face recognition with performance optimization”, Sensors, Vol.20, No.21, 6114, 2020.
[20] N. M. Dipu et al., “Deep learning based brain tumor detection and classification”, International Conference on Intelligent Technologies (CONIT), pp.1–6, 2021.
[21] M. M. Zahoor et al., “Brain Tumor MRI Classification Using a Novel Deep Residual and Regional CNN”, Biomedicines, Vol.12, No.7, 2024.
[22] N. Alemayehu, “Light Weight CNN for Classification of Brain Tumors from MRI Images”, arXiv preprint, Apr. 2025.
[23] Anonymous, “A hybrid deep CNN model for brain tumor image multi-classification”, BMC Medical Imaging. Jan., Art.21. Vol.24, 2024.
[24] Anonymous, “Enhancing brain tumor detection in MRI images through explainable AI using Grad?CAM with ResNet?50”, BMC Medical Imaging, 2024.
[25] B. Vimala et al., “BTC?fCNN: Fast Convolutional Neural Network for Multi?class Brain Tumor Classification”, Scientific Reports, Vol.13, 2023.
[26] P. S. Renjeni and B. Mukunthan, “Identification of Brain Tumor Using Projection Pursuit Bivariate Multilayer Perceptred Classification”, International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.9, No.5, pp.7–14, 2021. DOI: 10.26438/ijcse/v9i5.714.
[27] D. Ghosh and U. Roy, “Brain Tumor Detection from MRI Image Using Deep Learning”, International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.7, No.1, pp.142–149, 2019.
[28] M. M. Zahoor et al., “Brain Tumor MRI Classification Using a Novel Deep Residual and Regional CNN”, Biomedicines, Vol.12, No.7, 2024.
[29] N. Alemayehu, “Light Weight CNN for Classification of Brain Tumors from MRI Images”, arXiv preprint, Apr. 2025.
[30] B. Vimala et al., “BTC?fCNN: Fast Convolutional Neural Network for Multi?class Brain Tumor Classification”, Scientific Reports, Vol.13, 2023.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




