A Machine Learning Framework for Financial Fraud Detection Using Explainable Artificial Intelligence Techniques
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v13i5.1725Keywords:
Fraud detection, Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI), SHAP, LIME, SMOTEAbstract
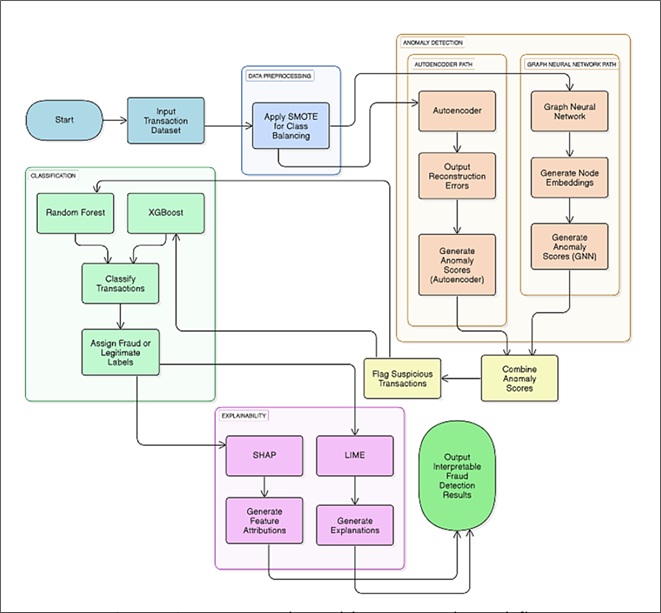
Detection of fraud in business has become increasingly significant with the intricacy and complexity of contemporary fraudulent schemes. This paper presents an exhaustive review of sophisticated approaches integrating machine learning, anomaly detection, and Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) for improving fraud detection systems. Primary preprocessing methods like SMOTE resolve class imbalance, whereas models like Autoencoders and Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) detect anomalous patterns in large and complex datasets efficiently. Classification techniques, like Random Forest and XGBoost, show great performance in detecting fraudulent transactions. Correspondingly, the integration of XAI methods such as SHAP and LIME completes the gap in between accuracy and transparency, finding solutions in order to regulate compliance and attain confidence in automated systems. Recent advances including generative AI models and secure mechanisms have vowed to balance predictive ability and data privacy. Though these developments are underway, scalability, real-time deployment, and expansion to keep up with growing fraud patterns continue to be challenges. This work identifies emerging trends, recognizes key research gaps, and proposes a research plan for creating scalable, interpretable, and adaptive financial fraud detecting systems
References
[1] K. Koo, M. Park, and B. Yoon, “A suspicious financial
transaction detection model using autoencoder and risk-based
approach,” IEEE Access, Vol.12, pp.68926–68939, 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3399824
[2] S. Bisht, S. Sengupta, I. Tewari, N. Bisht, K. Pandey, and A.
Upadhyay, “AI-Driven Tools Transforming The Banking
Landscape: Revolutionizing Finance,” In the Proceedings of the
2024 10th International Conference on Advanced Computing and
Communication Systems (ICACCS), IEEE, pp.934–938, 2024.
[3] P. Sharma, A. S. Prakash, and A. Malhotra, “Application of
Advanced AI Algorithms for Fintech Crime Detection,” In the
Proceedings of the 2024 15th International Conference on
Computing Communication and Networking Technologies
(ICCCNT), IEEE, pp.1–6, 2024.
[4] G. Konstantinidis and A. Gegov, “Deep Neural Networks for Anti
Money Laundering Using Explainable Artificial Intelligence,” In
the Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 12th International Conference
on Intelligent Systems (IS), IEEE, pp.1–6, 2024.
[5] T. H. Phyu and S. Uttama, “Enhancing Money Laundering
Detection Addressing Imbalanced Data and Leveraging
Typological Features Analysis,” In the Proceedings of the 2024
21st International Joint Conference on Computer Science and
Software Engineering (JCSSE), IEEE, pp.330–336, 2024.
[6] T. H. Phyu and S. Uttama, “Improving Classification
Performance of Money Laundering Transactions Using
Typological Features,” In the Proceedings of the 2023 7th
International Conference on Information Technology (InCIT),
IEEE, pp.520–525, 2023.
[7] C. Maree, J. E. Modal, and C. W. Omlin, “Towards responsible
AI for financial transactions,” In the Proceedings of the 2020
IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI),
IEEE, pp.16–21, 2020.
[8] Z. Chen, W. M. Soliman, A. Nazir, and M. Shorfuzzaman,
“Variational autoencoders and Wasserstein generative adversarial
networks for improving the anti-money laundering process,”
IEEE Access, Vol.9, pp.83762–83785, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3086359
[9] R. Desrousseaux, G. Bernard, and J. J. Mariage, “Profiling
money laundering with neural networks: A case study on
environmental crime detection,” In the Proceedings of the 2021
IEEE 33rd International Conference on Tools with Artificial
Intelligence (ICTAI), IEEE, pp.364–369, 2021.
[10] Z. Ereiz, “Predicting default loans using machine learning
(OptiML),” In the Proceedings of the 2019 27th
Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR), IEEE, pp.1–4, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TELFOR48224.2019.8971110
[11] H. N. Mohammed, N. S. Malami, S. Thomas, F. A. Aiyelabegan,
F. A. Imam, and H. H. Ginsau, “Machine learning approach to
anti-money laundering: A review,” In the Proceedings of the 2022
IEEE Nigeria 4th International Conference on Disruptive
Technologies for Sustainable Development (NIGERCON), IEEE,
pp.1–5, 2022.
[12] A. F. Mhammad, R. Agarwal, T. Columbo, and J. Vigorito,
“Generative & responsible AI-LLMs use in differential
governance,” In the Proceedings of the 2023 International
Conference on Computational Science and Computational
Intelligence (CSCI), IEEE, pp.291–295, 2023.
[13] E. Kurshan, H. Shen, and H. Yu, “Financial crime & fraud
detection using graph computing: Application considerations &
outlook,” In the Proceedings of the 2020 Second International
Conference on Transdisciplinary AI (TransAI), IEEE, pp.125–
130, 2020.
[14] A. El-Kilany, A. M. Ayoub, and H. M. El Kadi, “Detecting
Suspicious Customers in Money Laundering Activities Using
Weighted HITS Algorithm,” In the Proceedings of the 2024 5th
International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and
Control (AIRC), IEEE, pp.112–117, 2024.
[15] K. Balaji, “Artificial Intelligence for Enhanced Anti-Money
Laundering and Asset Recovery: A New Frontier in Financial
Crime Prevention,” In the Proceedings of the 2024 Second
International Conference on Intelligent Cyber Physical Systems
and Internet of Things (ICoICI), IEEE, pp.1010–1016, 2024.
[16] D. Cheng, Y. Ye, S. Xiang, Z. Ma, Y. Zhang, and C. Jiang, “Anti-
money laundering by group-aware deep graph learning,” IEEE
Trans. Knowl. Data Eng., Vol.35, No.12, pp.12444–12457, 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2023.3272396
[17] D. V. Kute, B. Pradhan, N. Shukla, and A. Alamri, “Deep learning
and explainable artificial intelligence techniques applied for
detecting money laundering – A critical review,” IEEE Access,
Vol.9, pp.82300–82317, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3086230
[18] D. V. Kute, B. Pradhan, N. Shukla, and A. Alamri, “Explainable
deep learning model for predicting money laundering
transactions,” Int. J. Smart Sens. Intell. Syst., Vol.17, No.1, 2024.
https://doi.org/10.2478/ijssis-2024-0027
[19] O. Kuiper, M. van den Berg, J. van der Burgt, and S. Leijnen,
“Exploring explainable AI in the financial sector: Perspectives of
banks and supervisory authorities,” In the Proceedings of the
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: 33rd Benelux
Conference on Artificial Intelligence, BNAIC/Benelearn 2021,
Esch-sur-Alzette, Luxembourg, Nov. 10–12, 2021, Revised
Selected Papers, Springer International Publishing, Vol.33,
pp.105–119, 2022.
[20] D. Vijayanand and G. S. Smrithy, “Explainable AI-enhanced
ensemble learning for financial fraud detection in mobile money
transactions,” Intelligent Decision Technologies, Art. no.
18724981241289751, 2024.
[21] F. Xu, H. Uszkoreit, Y. Du, W. Fan, D. Zhao, and J. Zhu,
“Explainable AI: A brief survey on history, research areas,
approaches and challenges,” In the Proceedings of the Natural
Language Processing and Chinese Computing: 8th CCF
International Conference, NLPCC 2019, Dunhuang, China, Oct.
9–14, 2019, Part II, Springer International Publishing, Vol.8,
pp.563–574, 2019.
[22] R. Alhajeri and A. Alhashem, “Using Artificial Intelligence to
Combat Money Laundering,” Intelligent Information
Management, Vol.15, No.4, pp.284–305, 2023.
https://doi.org/10.4236/iim.2023.154014
[23] S. K. Hashemi, S. L. Mirtaheri, and S. Greco, “Fraud detection in
banking data by machine learning techniques,” IEEE Access,
Vol.11, pp.3034–3043, 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3232287
[24] E. R. Mill, W. Garn, N. F. Ryman-Tubb, and C. Turner,
“Opportunities in real time fraud detection: An explainable
artificial intelligence (XAI) research agenda,” International
Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, Vol.14,
No.5, pp.1172–1186, 2023.
https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2023.01405121
[25] I. Psychoula, A. Gutmann, P. Mainali, S. H. Lee, P. Dunphy, and
F. Petitcolas, “Explainable machine learning for fraud detection,”
Computer, Vol.54, No.10, pp.49–59, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1109/MC.2021.3081249
[26] J. Vidya Sagar and S. Aquter Babu, “A Hybrid Machine Learning
Approach for Real-Time Fraud Detection in Online Payment
Transactions,” Library Progress International, Vol.44, No.3,
pp.26067–26090, 2024.
[27] Anirban Majumder, “Intelligent AI Agents for Fraud and Abuse
Detection”, International Journal of Computer Science and
Engineering, Vol.12, Issue.4, pp.1-7, 2025.
[28] Avinash Malladhi, “Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
in Forensic Accounting”, International Journal of Computer
Science and Engineering, Vol.10, Issue.7, pp.15-21, 2023
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




