Identification of Human Being using Periocular Biometrics with Multi-Layered Network
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v13i4.105110Keywords:
Periocular Biometrics, Human Identification, Covid-19, Security,, Security, Multi-layered NetworksAbstract
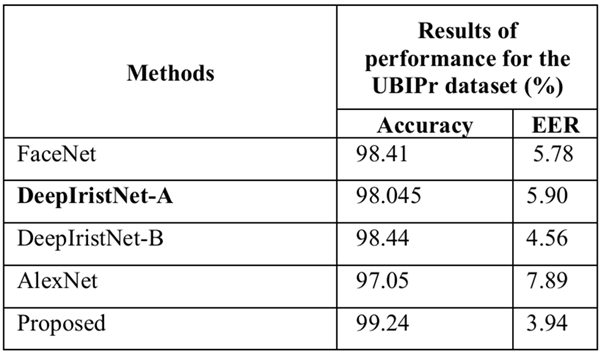
The coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) pandemic has significantly reduced people`s life expectancy and conveyed fears to people around the world. These requirements raise concerns about the long-term impact of wearing face masks and social marginalisation. This highlights the need for contactless biometry to check. Eye biometrics are the best option. Biometric characteristics-based personal identification systems are generally recommended for verifying the identity of people in public locations such as ATMs, banks, school visit systems, and airport immigration clearance systems. Compare it with other networks such as Face Net, Alexnet, DeepiristNet-A, DeepiristNet-B. recognition. The error rate is 3.39 times lower than the other errors.
References
[1] N. U. Ahmed, S. Cvetkovic, E. H. Siddiqi, and A. Nikiforov, "Combining iris and periocular biometrics for matching visible spectrum eye images," Pattern Recogn. Lett., vol. 91, pp. 11–16, 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2017.03.003.
[2] M. De Marsico, A. Petrosino, and S. Ricciardi, "Iris recognition through machine learning techniques: A survey," Pattern Recognit. Lett., vol. 82, pp. 106–115, Oct. 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2016.02.001.
[3] D. Woodard, G. Dozier, P. Miller, K. Bryant, and G. Glenn, "Genetic-based type ii feature extraction for periocular biometric recognition: less is more," in Proc. Int. Conf. Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Istanbul, Turkey, 2010, pp. 205–208, doi: 10.1109/ICPR.2010.59.
[4] D. Woodard, G. Dozier, P. Miller, K. Bryant, and G. Glenn, "Genetic-based type ii feature extraction for periocular biometric recognition: less is more," in Proc. Int. Conf. Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Istanbul, Turkey, 2010, pp. 205–208, doi: 10.1109/ICPR.2010.59.
[5] J. J. Winston and D. J. Hemanth, "A comprehensive review on iris image-based biometric system," Soft Comput., vol. 23, no. 19, pp. 9361–9384, Oct. 2019, doi: 10.1007/s00500-018-3497-y.
[6] F. Alonso-Fernandez and J. Bigun, "A survey on periocular biometrics research," Pattern Recogn. Lett., vol. 82, pp. 92–105, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2015.08.026.
[7] H. Proenca and C. N. Padole, "Periocular recognition: Analysis of performance degradation factors," in Proc. 5th IAPR Int. Conf. Biometrics (ICB), Mar. 2012, pp. 439–445, doi: 10.1109/ICB.2012.6199790.
[8] A. Ross and R. Sharma, "Periocular biometrics and its relevance to partially masked faces: A survey," Understanding, vol. 103583, Jan. 2023.
[9] U. Park and A. Ross, "Periocular Biometrics in the visible spectrum: A Feasibility study," in Proc. 3rd IEEE Int. Conf. Biometrics: Theory Applications and Systems (BTAS), Washington, DC, USA, 2009, pp. 153–158, doi: 10.1109/BTAS.2009.5339068.
[10] U. Park, R. Jillela, and A. Ross, "Periocular biometrics in the visible spectrum," IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur., vol. 6, no. 01, pp. 96–106, 2011, doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2010.2096810.
[11] K. K. Kumar and M. Pavani, "Periocular region-based age-invariant face recognition using a local binary pattern," in Microelectronics, Electromagnetics and Telecommunications, Singapore: Springer, 2019, pp. 713–720, doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-1906-8_72.
[12] P. Kumari and K. R. Seeja, "Periocular Biometrics: A survey," J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci., 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2019.06.003.
[13] G. Mahalingam and K. Ricanek Jr., "LBP-based periocular recognition on challenging face datasets," EURASIP J. Image Video Process., vol. 2013, no. 36, 2013, doi: 10.1186/1687-5281-2013-36.
[14] I. Nigam, M. Vatsa, and R. Singh, "Ocular biometrics: a survey of modalities and fusion approaches," Inf. Fusion, vol. 26, pp. 1–35, 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2015.03.005.
[15] K. B. Raja, R. Raghavendra, and C. Busch, "Binarized statistical features for improved iris and periocular recognition in the visible spectrum," in Proc. 2nd Int. Workshop Biometrics Forensics, Valletta, Malta, 2014, pp. 1–6, doi: 10.1109/IWBF.2014.6914249.
[16] L. Tiong, A. B. J. Teoh, Y. Lee, and A. J. N. T. Liong, "Periocular recognition in the wild with an orthogonal combination of local binary coded pattern in a dual-stream convolutional neural network," Appl. Sci., vol. 9, no. 13, p. 2709, 2019.
[17] L. Nie, A. Kumar, and S. Zhan, "Periocular recognition using unsupervised convolutional rbm feature learning," in Proc. Int. Conf. Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 2014, pp. 399–404.
[18] K. B. Raja, R. Raghavendra, and C. Busch, "Binarized statistical features for improved iris and periocular recognition in the visible spectrum," in Proc. Int. Workshop Biometrics Forensics (IWBF), 2014, pp. 1–6.
[19] K. B. Raja, R. Raghavendra, and C. Busch, "Biometric recognition of surgically altered periocular region: A comprehensive study," in Proc. Int. Conf. Biometrics (ICB), 2016, pp. 1–6.
[20] K. B. Raja, R. Raghavendra, and C. Busch, "Collaborative representation of deep sparse filtered features for robust verification of smartphone periocular images," in Proc. Int. Conf. Image Processing (ICIP), 2016, pp. 330–334.
[21] K. B. Raja, R. Raghavendra, and C. Busch, "Dynamic scale selected laplacian decomposed frequency response for cross-smartphone periocular verification in the visible spectrum," in Proc. Int. Conf. Information Fusion (Fusion), 2016, pp. 2206–2212.
[22] K. B. Raja, R. Raghavendra, and C. Busch, "Scale-level score fusion of steered pyramid features for cross-spectral periocular verification," in Proc. Int. Conf. Information Fusion (Fusion), 2017, pp. 1–7.
[23] R. Raghavendra, K. B. Raja, and C. Busch, "Collaborative representation of blur invariant deep sparse features for periocular recognition from smartphones," Image Vis. Comput., vol. 101, p. 103979, 2020.
[24] K. B. Raja, R. Raghavendra, M. Stokkenes, and C. Busch, "Smartphone authentication system using periocular biometrics," in Proc. Int. Conf. Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), 2014, pp. 1–8.
[25] K. B. Raja, R. Raghavendra, M. Stokkenes, and C. Busch, "Fusion of face and periocular information for improved authentication on smartphones," in Proc. Int. Conf. Information Fusion (Fusion), 2015, pp. 2115–2120.
[26] K. B. Raja, R. Raghavendra, M. Stokkenes, and C. Busch, "Multi-modal authentication system for smartphones using face, iris, and periocular," in Proc. Int. Conf. Biometrics (ICB), 2015, pp. 143–150.
[27] K. B. Raja, R. Raghavendra, V. K. Vemuri, and C. Busch, "Smartphone-based visible iris recognition using deep sparse filtering," Pattern Recognit. Lett., vol. 57, pp. 33–42, 2015.
[28] R. Raghavendra and C. Busch, "Learning deeply coupled autoencoders for smartphone-based robust periocular verification," in Proc. Int. Conf. Image Processing (ICIP), 2016, pp. 325–329.
[29] E. Luz, G. Moreira, L. A. Zanlorensi Junior, D. Menotti, and R. Laroca, "Deep periocular representation aiming video surveillance," Pattern Recognit. Lett., vol. 114, pp. 2–12, 2018.
[30] P. Kumari and K. R. Seeja, "A novel periocular biometrics solution for authentication during the COVID-19 pandemic situation," J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput., pp. 10321–10337, 2021.
[31] P. Kumari and K. R. Seeja, "An optimal feature enriched region of interest(ROI) extraction for the periocular biometric system," Multimedia Tools Appl., 2021.
[32] H. Proenca and C. Padole, "Ocular biometrics by score-level fusion of disparate experts," IEEE Trans. Image Process., vol. 23, 2014.
[33] H. Proenca and J. C. Briceño, "Periocular biometrics: constraining the elastic graph matching algorithm to biologically plausible distortions," IET Biometrics, vol. 3, pp. 167–175, 2014.
[34] H. Proença and J. C. Neves, "Deep-PRWIS: Periocular recognition without the iris and sclera using deep learning frameworks," IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur., vol. 13, pp. 888–896, 2018.
[35] H. Proença and J. C. Neves, "A reminiscence of mastermind: Iris/periocular biometrics by in-set CNN iterative analysis," IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur., vol. 14, pp. 1702–1712, 2019.
[36] Z. Zhao and A. Kumar, "Accurate periocular recognition under a less constrained environment using semantics-assisted convolutional neural network," IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur., vol. 12, pp. 1017–1030, 2017.
[37] Z. Zhao and A. Kumar, "Improving periocular recognition by explicit attention to critical regions in deep neural networks," IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur., vol. 13, pp. 2937–2952, 2018.
[38] F. Alonso-Fernandez, K. Hernandez-Diaz, and J. Bigun, "Cross-spectral periocular recognition with conditional adversarial networks," in Proc. Int. Joint Conf. Biometrics (IJCB), 2020.
[39] M. C. Kim, J. H. Koo, S. W. Cho, N. R. Baek, and Park, "Convolutional neural network-based periocular recognition in surveillance environments," IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 57291–57310, 2018.
[40] Q. Zhang, H. Li, Z. Sun, and T. Tan, "Deep feature fusion for iris and periocular biometrics on mobile devices," IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur., vol. 13, pp. 2897–2912, 2018.
[41] R. Derakhshani, N. Reddy, and A. Rattani, "Robust subject-invariant feature learning for ocular biometrics in the visible spectrum," in Proc. Int. Conf. Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), 2019, pp. 1–9.
[42] R. Garg, Y. Baweja, S. Ghosh, R. Singh, M. Vatsa, and N. Ratha, "Heterogeneity aware deep embedding for mobile periocular recognition," in Proc. Int. Conf. Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), 2018, pp. 1–7.
[43] N. Reddy, A. Rattani, and R. Derakhshani, "Comparison of deep learning models for biometric-based mobile user authentication," in Proc. Int. Conf. Biometrics Theory, Applications, and Systems (BTAS), 2018, pp. 1–6.
[44] Y. G. Jung, C. Y. Low, J. Park, and A. B. J. Teoh, "Periocular recognition in the wild with generalized label smoothing regularization," Signal Process. Lett., vol. 27, pp. 1455–1459, 2020.
[45] D. Woodard, G. Dozier, P. Miller, K. Bryant, and G. Glenn, "Genetic-based type ii feature extraction for periocular biometric recognition: less is more," in Proc. Int. Conf. Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Istanbul, Turkey, 2010, pp. 205–208, doi: 10.1109/ICPR.2010.59.
[46] N. Reddy, A. Rattani, and R. Derakhshani, "Generalizable deep features for ocular biometrics," Image Vis. Comput., vol. 103, p. 103996, 2020.
[47] L. C. O. Tiong and A. B. J. Teoh, "Periocular Recognition in the Wild with Orthogonal Combination of Local Binary Coded Pattern in Dual- stream Convolutional Neural Network," Mar. 2019, doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1902.06383.
[48] D. R. Bhamare and P. S. Patil, "Person Identification System Using Periocular Biometrics Based on Hybrid Optimal Dense Capsule Network," Int. J. Intell. Syst. Technol. Appl., doi: 10.1142/S0218001423560268.
[49] F. Alonso-Fernandez and J. Bigun, "PERIOCULAR BIOMETRICS: DATABASES, ALGORITHMS, AND DIRECTIONS," Halmstad University, Halmstad, Sweden.
[50] A. Krizhevsky and I. Sutskever, "ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks," Commun. ACM, vol. 60, no. 6, pp. 84–90, doi: 10.1145/3065386.
[51] A. Alahmadi, M. Hussain, and H. Aboalsamh, "LDA-CNN: Linear Discriminant Analysis Convolution Neural Network for Periocular Recognition in the Wild," Mathematics, vol. 10, no. 23, p. 4604, Dec. 2022.
[52] L. A. Zanlorensi, R. Laroca, D. R. Lucio, and D. Menotti, "A new periocular dataset collected by mobile devices in unconstrained scenarios," Sci. Rep., vol. 12, no. 17989, 2022, doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22811-y.
[53] S. Ramachandra and S. Ramachandran, "Region-specific and sub-image based neighbor gradient feature extraction for robust periocular recognition," J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci., vol. 34, no. 1, Jul. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2022.07.013.
[54] X. Xu, J. Liang, C. Chen, and Z. Hou, "Weighted similarity and distance metric learning for unconstrained face verification with 3D formalization," 2019, doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2018.6327.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




