Enhancing Agility and Security for Small and Medium Businesses through Cloud Technologies
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v13i2.5763Keywords:
Cloud Computing, Small Businesses, Cloud Technologies, Remote Servers, AWS, SLAsAbstract
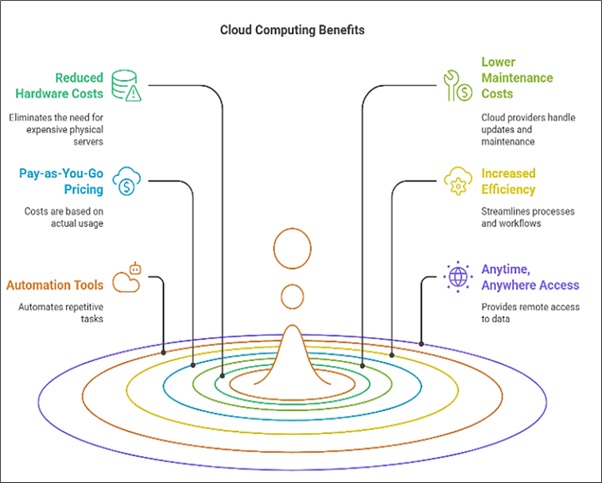
Cloud computing is a more current approach to managing long-term business needs. Cloud computing is conceivable thanks to the rapid advancements of the web and next-generation laptops. Cloud computing supports private businesses in several ways. Backs up and stays updated with company information, runs schedulers, and works on data sharing. Small organization owners need to get what they need in today's ever-changing business environment, whether on their PCs, tablets, or phones, in the workplace, in the field, or movement. Cloud computing allows customers to access information from any area with a web connection. Cloud logging targets private companies by leveling the playing field. It will enable them to access trending innovations used by large companies without significant out-of-pocket expenses. Independent businesses can store information, run applications, and train teams remotely, supporting productivity and eliminating IT costs. The benefits of the Cloud also offer adaptability, so organizations can change their resources according to their interests without putting too much effort into the foundations. Additionally, cloud phases provide information security and hardening, safeguarding critical business data. By adopting cloud computing, private companies gain adaptability, cost reserve funds, and greater efficiency, making them innovative enterprises for development. This paper will discuss how the Cloud has affected the small business industries.
References
[1] I. Foster, Y. Zhao, I. Raicu, and S. Lu, “Cloud Computing and Grid Computing 360-Degree Compared,” Journal of Grid Computing, Vol.6, No.3, pp.1–10, 2008.
[2] R. Solanki, Principles of Data Mining, 1st ed., McGraw-Hill, India, pp.386–398, 1998.
[3] M. Mohammad, “Performance Impact of Addressing Modes on Encryption Algorithms,” in Proc. 2001 IEEE International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD 2001), USA, pp.542–545, 2001.
[4] K. Gupta, “A Proposed New Approach for Cloud Environment Using Cryptic Rules,” in Advances in Cloud Computing, 1st ed., ISROSET Publisher, India, pp.542–545, 2016.
[5] M. Jensen, J. Schwenk, N. Gruschka, and L. L. Iacono, “On Technical Security Issues in Cloud Computing,” IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, Vol.1, No.1, pp.109–116, 2009.
[6] S. Sharma and L. Gupta, “A Novel Approach for Cloud Computing Environment,” International Journal of Computer Engineering, Vol.4, No.12, pp.1–5, 2014.
[7] R. L. Grossman, “The Case for Cloud Computing,” IT Professional, Vol.11, No.2, pp.23–27, 2009.
[8] A. Kambil, “A Head in the Cloud,” Journal of Business Strategy, Vol.30, No.4, pp. 58–59, 2009.
[9] V. Mongia and D. Kumar, “Resource Allocation in Cloud Computing: A Review,” International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, June, Vol.6, Special Issue 5, 2018.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




