YouTube Comments Analyzer Using Natural Language Processing And Artificial Intelligence
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v12i12.114Keywords:
Natural language processing, Analyze, Real-time Data acquisition, Human Sentiments, YouTube, Comments, Videos, Digital Media CreatorsAbstract
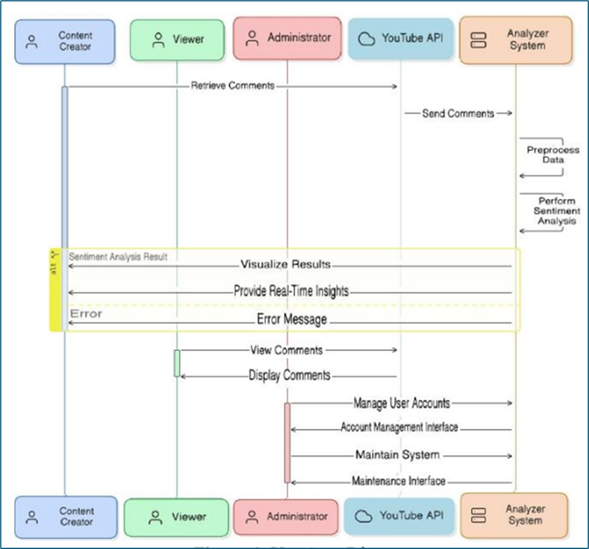
The exponential growth of online video content has propelled YouTube to the forefront of digital media platforms, where creators and viewers converge in a vibrant ecosystem. However, amidst the proliferation of videos, the accompanying surge in viewer comments poses a significant challenge for content creators and researchers alike. Manually sifting through this deluge of comments to gauge sentiment and understand audience feedback is increasingly untenable. To address this challenge, this manuscript introduces an automated tool, the YouTube Comment Analyzer, designed to efficiently extract and analyze comments on YouTube videos, categorizing them based on sentiment.
References
[1] Pak, A., & Paroubek, P., “Twitter as a Corpus for Sentiment Analysis and Opinion Mining.” Proceedings of the International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, pp.1320-1326, 2010.
[2] Thelwall, M., Sud, P., & Vis, F., “Commenting on YouTube Videos: From Guatemalan Rock to El Big Bang.” Journal ofthe American Society for Information Science and Technology, Vol.63, Issue.3, pp.616-629, 2012.
[3] Sarker, A., Belousov, M., Friedrichs, J., Hakala, K., Kiritchenko, S., Mehryary, F., ... & Xu, J., “Data and Systems for Sentiment Analysis in Social Media.” Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 88, pp.1-12, 2019.
[4] Kannan, A., & Gurusamy, S., “Preprocessing Techniques for Text Mining.” International Journal ofComputer Science and Information Technologies, Vol.5, Issue.1, pp.228-233, 2014.
[5] Keim, D., Kohlhammer, J., Ellis, G., & Mansmann, F., “Mastering the Information Age: Solving Problems with Visual Analytics.” Eurographics Association, 2013.
[6] Pang, B., Lee, L., &Vaithyanathan, S., “Thumbs Up? Sentiment Classification Using Machine Learning Techniques.” Proceedings ofthe ACL-02 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp.79-86, 2002.
[7] Jain, S., & Dahiya, K., “YouTube Data Analysis: A Case Study on Sentiment Analysis ofYouTube Videos and Comments.” International Journal ofComputer Applications, 176(6), pp.1-5, 2017.
[8] Cambria, E., Schuller, B., Xia, Y., & Havasi, C., “NewAvenues in Opinion Mining and Sentiment Analysis.” IEEE Intelligent Systems, Vol.28, Issue.2, pp.15-21, 2017.
[9] Cui, W., Wu, Y., Liu, S., Wei, F., Zhou, M. X., & Qu, H., “Context-Preserving Dynamic Word Cloud Visualization.” IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol.16, Issue.6, pp.1215-1224, 2010.
[10] Zhang, L., Wang, S., & Liu, B., “Deep Learning for Sentiment Analysis: A Survey.” Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 8(4), e1253, 2018.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




