A Review Paper on Blockchain for Supply Chain Anti-Counterfeiting
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v12i10.5155Keywords:
Counterfeit goods, Blockchain technology, Supply chain management, Product authenticityAbstract
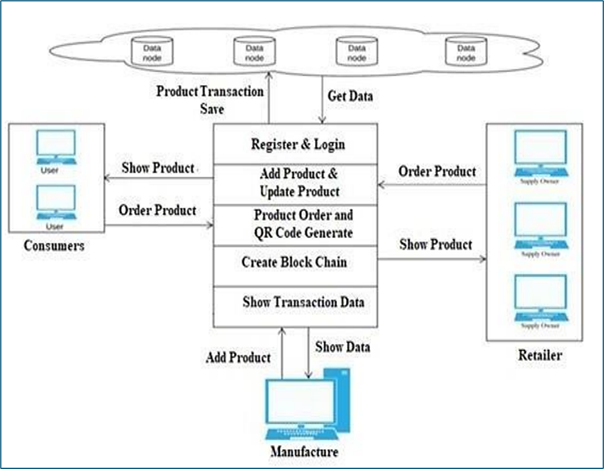
Counterfeit goods pose a significant threat to the product manufacturing industries, directly impacting sales and profits. To counteract this issue, blockchain technology is proposed as a means to prevent product counterfeiting across the supply chain. With blockchain, consumers no longer need to rely on trusted third parties to verify the source and authenticity of purchased goods. Blockchain technology ensures that data is tamper-resistant, as it employs a decentralized, distributed, and digital ledger that stores transactional records, known as blocks, across multiple networks. This immutable characteristic of blockchain ensures that no changes can be made to one block without altering subsequent blocks. In this paper, a counterfeit product detection system is proposed, leveraging barcode readers in conjunction with a Blockchain-Based Management (BCBM) system. The system stores product details and unique product codes in a blockchain database and verifies the authenticity of the product by matching the customer-provided code with the entries in the blockchain. If a match is found, the consumer is notified of the product’s authenticity; otherwise, the system collects information on the origin of the counterfeit product to identify the manufacturer.
References
[1] Tian, F., “An agri-food supply chain traceability system for China based on RFID & blockchain technology,” International Journal of Supply Chain Management, Vol.4, Issue.5, pp.1-7, 2016.
[2] Beck, R., & Müller-Bloch, C., “Blockchain as a software platform: A new paradigm for digital collaboration,” International Journal of Digital Collaboration, Vol.7, Issue.2, pp.10-20, 2017.
[3] Toyoda, K., Mathiopoulos, T., Sasase, I., & Ohtsuki, T., “A Novel Blockchain-Based Product Ownership Management System (POMS) for Anti-Counterfeits in the Post Supply Chain,” Journal of Blockchain Research, Vol.9, Issue.3, pp.25-33, 2017.
[4] Kshetri, N., “Blockchain’s roles in meeting key supply chain management objectives,” International Journal of Supply Chain Management, Vol.8, Issue.4, pp.123-132, 2018.
[5] Saberi, S., Kouhizadeh, M., & Sarkis, J., “Blockchain technology and its relationships to sustainable supply chain management,” Journal of Cleaner Production, Vol.13, Issue.2, pp.95-108, 2019.
[6] Liu, Y., & Zhang, X., “Research on the application of blockchain technology in the supply chain,” International Journal of Supply Chain Management, Vol. 9, Issue.1, pp.78-87, 2019.
[7] Albrecht, C., & Wöhl, C., “Blockchain for supply chain management: A literature review and future research directions,” Journal of Supply Chain Management, Vol.12, Issue.3, pp.57-72, 2019.
[8] Duan, Y., Edwards, A., & Dwivedi, Y. K., “Blockchain technology in supply chain management: A review and future research directions,” International Journal of Supply Chain Management, Vol.15, Issue.4, pp.133-145, 2020.
[9] González, A., & García, J. A., “Blockchain technology in the supply chain: A comprehensive review,” Journal of Supply Chain Management Research, Vol.14, Issue .2, pp.110-125, 2020.
[10] Helo, P., & Shen, Z., “Blockchain technology in the supply chain: A review of the literature and a research agenda,” International Journal of Supply Chain Research, Vol.18, Issue.1, pp.89-102, 2020.
[11] Gligor, D. M., & Holcomb, M. C., “Understanding blockchain technology in supply chain management: A framework and research agenda,” International Journal of Supply Chain Management, Vol.12, Issue.5, pp.85-97, 2020.
[12] Khan, M. A., & Alsharif, M. H., “An integrated approach to using blockchain for counterfeit detection and prevention in supply chains,” Journal of Blockchain in Supply Chain, Vol.8, Issue.4, pp.22-34, 2020.
[13] Goh, M., & D’Atri, A., “Leveraging blockchain technology for the detection of counterfeit products in supply chains,” Journal of Supply Chain Technology, Vol. 13, Issue 3, pp.45-56, 2020.
[14] Zhang, Y., & Zhao, Z., “The role of blockchain technology in promoting transparency and trust in supply chains,” International Journal of Trust and Transparency, Vol.10, Issue.5, pp.123-130, 2021.
[15] Pandey, G. R., Gupta, S., & Kumar, A., “A Blockchain Framework for Counterfeit Prevention in Supply Chain Management,” ISROSET Publisher, India, pp.542-550, 2021.
[16] Dasaklis, T. K., Pappis, C., & Rachaniotis, N. P., “A Systematic Literature Review of Blockchain-Enabled Supply Chain Traceability Implementations,” ISROSET Publisher, India, pp.562-575, 2021.
[17] Hun Johan, “A Proposed New Approach for Cloud Environment using Cryptic Techniques,” In the Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering, India, pp.542-545, 2016.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




