Development of a Model for the Detection of Malicious Activities on Edge Computing
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v12i8.1824Keywords:
Edge Computing, Malicious packets, recurrent neural network, Random Forest ClassifierAbstract
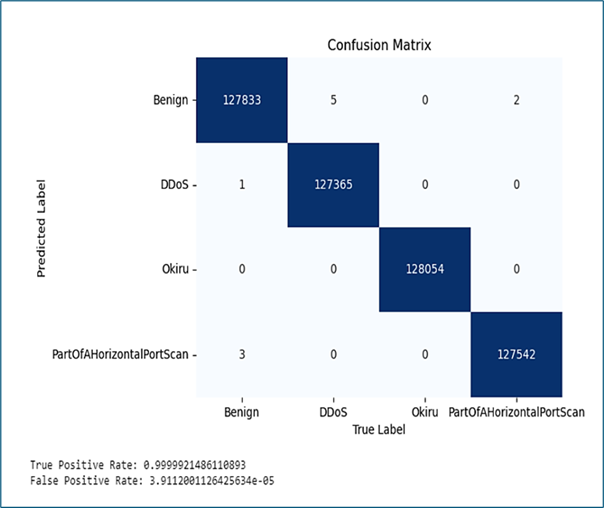
The unique characteristics of edge computing, such as limited resources and decentralized architecture, pose distinct challenges to traditional security measures. As the adoption of edge computing continues to proliferate across diverse domains, the security of edge devices becomes a paramount concern. This paper outlines a comprehensive approach for the detection of malicious activities (DDoS, Okiru and PartofHorizontalPortScan) on edge computing devices. The proposed solution leverages a combination of anomaly detection, Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) algorithm, and behaviour analysis tailored to the constraints of edge devices. By considering the specific context of edge environments, the model aims to distinguish between normal and malicious behaviour in edge computing, offering a proactive defence against emerging threats. Furthermore, the integration of threat intelligence feeds enhances the system`s ability to adapt to evolving attack vectors. The efficiency of the proposed solution ensures minimal impact on the performance of resource-constrained edge devices. This paperwork contributes to the ongoing efforts to fortify the security of edge computing ecosystems. By addressing the unique challenges associated with these devices, the proposed RNN algorithm provides a robust and adaptive framework for the detection and mitigation of malicious activities in edge computing, safeguarding the integrity and reliability of edge computing applications with an accuracy of 99.9%.
References
[1] J. Abawajy, S. Huda, S. Sharmeen, M. M. Hassan, and A. Almogren, "Identifying cyber threats to mobile-IoT applications in edge computing paradigm," Future Generation Computer Systems, Vol.89, pp.525-538, 2018.
[2] A. Anand, S. Patil, and P. Kulkarni, "A survey on edge computing security: Threats, attacks, and defenses," Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, Vol.12, No.5, pp.4871-4891, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03246-6
[3] W. G. Hatcher, J. Booz, J. McGiff, C. Lu, and W. Yu, "Edge computing based machine learning mobile malware detection," 2017.
[4] R. H. Hsu et al., "A privacy-preserving federated learning system for android malware detection based on edge computing," in 2020 15th Asia Joint Conference on Information Security (AsiaJCIS), pp.128-136, 2020.
[5] H. M. Kim and K. H. Lee, "IIoT malware detection using edge computing and deep learning for cybersecurity in smart factories," Applied Sciences, Vol.12, No.15, pp.7679, 2022.
[6] K. J. Kim and J. H. Kim, "A survey of security threats and countermeasures in edge computing," Journal of Supercomputing, Vol.76, No.8, pp.5834-5864, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03154-5
[7] Y. J. Kim, C. H. Park, and M. Yoon, "FILM: filtering and machine learning for malware detection in edge computing," Sensors, Vol.22, No.6, pp.2150, 2022.
[8] W. Lian, G. Nie, Y. Kang, B. Jia, and Y. Zhang, "Cryptomining malware detection based on edge computing-oriented multi-modal features deep learning," China Communications, Vol.19, No.2, pp.174-185, 2022.
[9] A. Libri, A. Bartolini, and L. Benini, "pAElla: Edge AI-based real-time malware detection in data centers," IEEE Internet of Things Journal, Vol.7, No.10, pp.9589-9599, 2020.
[10] A. Mahindru and H. Arora, "Dnndroid: Android malware detection framework based on federated learning and edge computing," in International Conference on Advancements in Smart Computing and Information Security, Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, pp.96-107, 2022.
[11] Y. Shen, S. Shen, Z. Wu, H. Zhou, and S. Yu, "Signaling game-based availability assessment for edge computing-assisted IoT systems with malware dissemination," Journal of Information Security and Applications, Vol.66, pp.103140, 2022.
[12] Z. Tian et al., "Real-time lateral movement detection based on evidence reasoning network for edge computing environment," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, Vol.15, No.7, pp.4285-4294, 2019.
[13] Y. Wang, L. Zhang, C. Xie, and Q. Wu, "A survey of security and privacy issues in edge computing," IEEE Network, Vol.34, No.6, pp.164-172, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.011.2000184
[14] Y. Yang, Y. Liu, C. Wang, and X. Tang, "A dynamic malicious activity detection scheme for edge computing based on deep learning," IEEE Access, Vol.8, pp.220217-220231, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3048144
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




