Prediction of Cotton and Tomato Leaf Disease using Ensemble Learning Algorithm
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v12i8.1017Keywords:
Cotton and Tomato leaves, Disease Prediction, Digital Image Processing, CNN, Transfer LearningAbstract
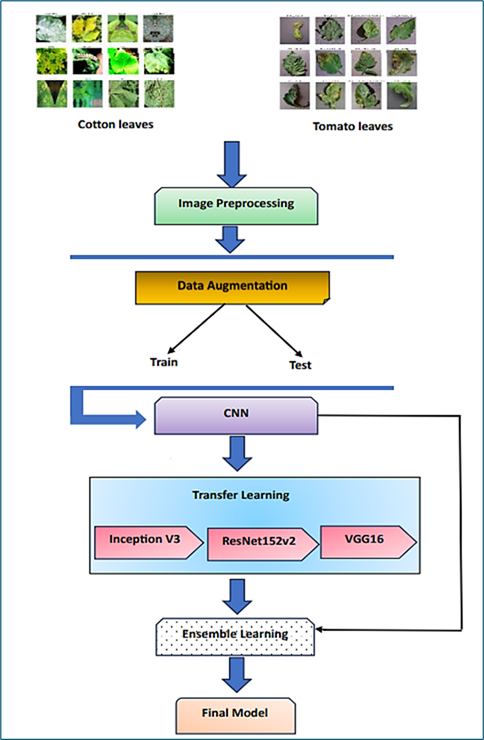
Agriculture, one of the primary and basic need for living, plays a vital role in the global economy. With growth in newer technology, plants are also more susceptible to new and divergent type of diseases. This type of disease affects the plants leaves and ultimately decreases its yield. This research paper focuses on industrial crop Cotton and food crop Tomato diseased leaf prediction by the framers. It classifies six varieties of cotton leaf diseases and ten varieties of tomato leaf diseases. The approach leverages image processing techniques, transfer learning with CNN techniques and ensemble techniques to classify images of cotton and tomato plant leaves. The main motivation of this research work is to help the farmers predict healthy and infected plant leaves in their farm land with the motivation of implementing sensors in their field. It also encourages future generations to be aware of such diseases in plant leaves and help to eradicate such fungal and viral disease in plants.
References
[1] Kumar, Sandeep, et al. "A comparative analysis of machine learning algorithms for detection of organic and nonorganic cotton diseases." Mathematical Problems in Engineering Vol.2021 Issue. 790171, pp.1-18, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/1790171
[2] Liu, J.; Wang, X. Tomato Diseases and Pests Detection Based on Improved Yolo V3 Convolutional Neural Network. Front. Vol.2020, Issue.11, pp.1–12. 2020. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00898
[3] Kumar, Raj, et al. "A Systematic analysis of machine learning and deep learning based approaches for plant leaf disease classification: a review." Journal of Sensors Vol.2022, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3287561
[4] Arivazhagan, Sai, et al. "Detection of unhealthy region of plant leaves and classification of plant leaf diseases using texture features." Agricultural Engineering International: CIGR Journal Vol.15, Issue.1, pp.211-217, 2013.
[5] Shubham, Bavaskar., V., R., Ghodake., Gayatri, S, Deshmukh., Pranav, Chillawar., Atul, B., Kathole. Image Classification Using Deep Learning Algorithms for Cotton Crop Disease Detection, 2022. doi: 10.1109/icdcece53908.2022.9792911
[6] Susa, Julie Ann B., et al. "Deep learning technique detection for cotton and leaf classification using the YOLO algorithm." 2022 International Conference on Smart Information Systems and Technologies (SIST). IEEE, 2022.
[7] Karunanidhi, Bavithra, et al. "Plant disease detection and classification using deep learning CNN algorithms." 2022 IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies (CONECCT). IEEE, 2022.
[8] Ali, Anjum, et al. "A Comparative Study Of Deep Learning Techniques For Boll Rot Disease Detection In Cotton Crops." Agricultural Sciences Journal 5.1 Vol.5, Issue.1, pp.58-71, 2023.
[9] Shoaib, Muhammad, et al. "Deep learning-based segmentation and classification of leaf images for detection of tomato plant disease." Frontiers in Plant Science Vol.13, 1031748, 2022
[10] Azath M., Melese Zekiwos, Abey Bruck, "Deep Learning-Based Image Processing for Cotton Leaf Disease and Pest Diagnosis", Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Vol.2021, pp.1-10, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9981437
[11] Kumbhar, Shantanu, et al. "Farmer buddy-web based cotton leaf disease detection using CNN." Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res., Vol.14, Issue.11, pp.2662-2666, 2019.
[12] Jenifa, A., R. Ramalakshmi, and V. Ramachandran. "Cotton leaf disease classification using deep convolution neural network for sustainable cotton production." 2019 IEEE international conference on clean energy and energy efficient electronics circuit for sustainable development (INCCES). IEEE, 2019.
[13] Patil, Bhagya M., and Vishwanath Burkpalli. "A perspective view of cotton leaf image classification using machine learning algorithms using WEKA." Advances in Human-Computer Interaction 2021, pp.1-15, 2021.
[14] Vasavi, Pallepati, Arumugam Punitha, and T. Venkat Narayana Rao. "Crop leaf disease detection and classification using machine learning and deep learning algorithms by visual symptoms: A review." International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering Vol.12.2, 2079, 2022.
[15] Azfar, Saeed, et al. "IoT-Based Cotton Plant Pest Detection and Smart-Response System." Applied Sciences Vol.13, Issue.3, pp.18-51, 2023.
[16] Mim, Tahmina Tashrif, et al. "Leaves diseases detection of tomato using image processing." 2019 8th international conference system modeling and advancement in research trends (SMART). IEEE, 2019.
[17] Thangaraj, Rajasekaran, et al. "Artificial intelligence in tomato leaf disease detection: a comprehensive review and discussion." Journal of Plant Diseases and Protection, Vol.129, Issue.3, pp.469-488, 2022.
[18] Ashok, Surampalli, et al. "Tomato leaf disease detection using deep learning techniques." 2020 5th International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES). IEEE, 2020.
[19] Agarwal, Mohit, et al. "ToLeD: Tomato leaf disease detection using convolution neural network." Procedia Computer Science Vol.167, pp.293-301, 2020.
[20] Basavaiah, Jagadeesh, and Audre Arlene Anthony. "Tomato leaf disease classification using multiple feature extraction techniques." Wireless Personal Communications Vol.115, Issue.1, pp.633-651, 2020.
[21] S. U. Maheswari and S. S. Dhenakaran, "Aspect based Fuzzy Logic Sentiment Analysis on Social Media Big Data," 2020 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Chennai, India, pp.0971-0975, 2020. doi: 10.1109/ICCSP48568.2020.9182174.
[22] Serosh Karim “Cotton leaf disease dataset”, kaggle, pp.1-16, 2021.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




