Advancements and Challenges in Fake News Detection using Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v12i7.4852Keywords:
Fake News Detection, Textual Feature ExtractionAbstract
The rapid proliferation of fake news across digital platforms has emerged as a challenging task, undermining public discourse, and compromising public trust in media. Initially, the detection efforts focused on textual features using traditional machine learning algorithms, which, despite their effectiveness, were limited by the manual and time-consuming process of feature extraction. The advent of deep learning heralded a significant shift, with Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) offering enhanced capabilities in capturing the nuanced interplay of textual elements. Parallelly, the examination of visual features through multimodal methods demonstrated the importance of incorporating images and videos, further refined by Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) and attention mechanisms for superior accuracy. However, challenges persist in integrating and fully utilizing multimodal information, particularly in addressing the limitations of deep versus shallow feature analysis and the adaptability of models across diverse scenarios. This paper synthesizes the methodologies, findings, and critical evaluations of these approaches, highlighting the advancements and identifying areas for future research in the detection of fake news.
References
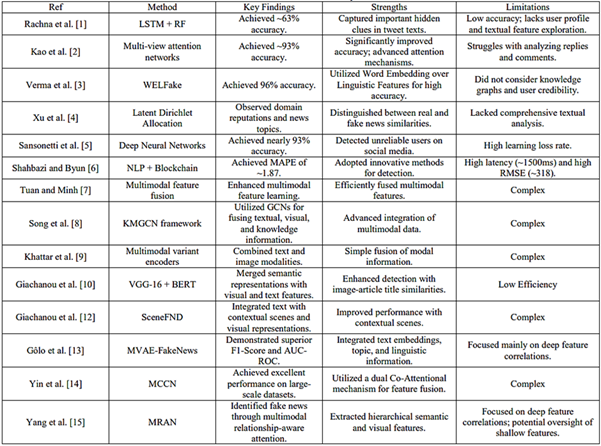
[1] Jain, Rachna & Jain, Deepak & Dharana, & Sharma, Nitika. Fake News Classification: A Quantitative Research Description. ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing, 2022. 21. 1-17. 10.1145/3447650.
[2] S. Ni, J. Li and H. -Y. Kao, "MVAN: Multi-View Attention Networks for Fake News Detection on Social Media," in IEEE Access, Vol.9, pp.106907-106917, 2021. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3100245.
[3] P. K. Verma, P. Agrawal, I. Amorim and R. Prodan, "WELFake: Word Embedding Over Linguistic Features for Fake News Detection," in IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, Vol.8, No.4, pp.881-893, 2021. doi: 10.1109/TCSS.2021.3068519.
[4] K. Xu, F. Wang, H. Wang and B. Yang, "Detecting fake news over online social media via domain reputations and content understanding," in Tsinghua Science and Technology, Vol.25, No.1, pp.20-27, 2020. doi: 10.26599/TST.2018.9010139.
[5] G. Sansonetti, F. Gasparetti, G. D’aniello and A. Micarelli, "Unreliable Users Detection in Social Media: Deep Learning Techniques for Automatic Detection," in IEEE Access, Vol.8, pp.213154-213167, 2020. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3040604.
[6] Z. Shahbazi and Y. -C. Byun, "Fake Media Detection Based on Natural Language Processing and Blockchain Approaches," in IEEE Access, Vol.9, pp.128442-128453, 2021. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3112607.
[7] N. M. Duc Tuan and P. Quang Nhat Minh, "Multimodal Fusion with BERT and Attention Mechanism for Fake News Detection," 2021 RIVF International Conference on Computing and Communication Technologies (RIVF), Hanoi, Vietnam, pp.1-6, 2021. doi: 10.1109/RIVF51545.2021.9642125.
[8] Song, Chenguang, et al. "Knowledge augmented transformer for adversarial multidomain multiclassification multimodal fake news detection." Neurocomputing 462, pp.88-100, 2021.
[9] Khattar, Dhruv, et al. "Mvae: Multimodal variational autoencoder for fake news detection." The world wide web conference. 2019.
[10] Giachanou, Anastasia, Guobiao Zhang, and Paolo Rosso. "Multimodal fake news detection with textual, visual and semantic information." Text, Speech, and Dialogue: 23rd International Conference, TSD 2020, Brno, Czech Republic, September, pp.8–11, 2020. Proceedings 23. Springer International Publishing, 2020.
[11] Wang, Y., Ma, F., Jin, Z., Yuan, Y., Xun, G., Jha, K., et al., Eann: Event adversarial neural networks for multi-modal fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 24th Acm sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery & data mining, pp.849–857, 2018.
[12] Zhang, Guobiao, Anastasia Giachanou, and Paolo Rosso. "SceneFND: Multimodal fake news detection by modelling scene context information." Journal of Information Science (2022): 01655515221087683.
[13] Gôlo, Marcos Paulo Silva, et al. "One-class learning for fake news detection through multimodal variational autoencoders." Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 122, 2023: 106088.
[14] Yin, Chunyan, and Yongheng Chen. "Multi-Modal Co-Attention Capsule Network for Fake News Detection." Optical Memory and Neural Networks 33.1, pp.13-27, 2024.
[15] Yang, Hongyu, et al. "MRAN: Multimodal relationship-aware attention network for fake news detection." Computer Standards & Interfaces 89, 103822, 2024.
[16] Mridha, Muhammad F., et al. "A comprehensive review on fake news detection with deep learning." IEEE access 9, pp.156151-156170, 2021.
[17] Zhou, Xinyi, and Reza Zafarani. "A survey of fake news: Fundamental theories, detection methods, and opportunities." ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 53.5, pp.1-40, 2020.
[18] Hangloo, Sakshini, and Bhavna Arora. "Fake News Detection Tools and Methods--A Review." arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.11185, 2021.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




