NMOS Linear Image Sensors: A Review of Data Acquisition and Monitoring
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v12i6.5054Keywords:
NMOS, Acquisition and MonitoringAbstract
This paper analyzes data acquisition and monitoring techniques used with negative-metal-oxide semiconductor (NMOS) linear image sensors. NMOS sensors have gained significant attention in various fields due to their advantages in terms of sensitivity, dynamic range, and low noise characteristics. Through a systematic review, the paper explores the fundamental characteristics of NMOS sensors, including their operation, sensitivity, and limitations. Data acquisition techniques will cover readout circuits, sensor resolution, timing characteristics and monitoring stratergies. A microcontroller can receive the gathered data and store it for later use
References
[1] Javier Pacheco-Labrador, Alejandro Ferrero and M. Pilar Mart´?n, ”Environmental Remote Sensing and Spectroscopy” Laboratory (SpecLab), Instituto de Econom´?a, Geograf´?a y Demograf´?a, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cient´?fica (CSIC), C/ Albasanz 26-28, 28037 Madrid, Spai.
[2] A. Fernandes, J. G. Rocha, G. Minas, ”Smart-Pixel Array for Imaging Sensors”, Dept. of Industrial Electronics University of Minho Campus de Azurem, 4800-058 Guimaraes, Portugal, IEEE International Confer- ´ ence,2007 1-4244-1378-8/07.
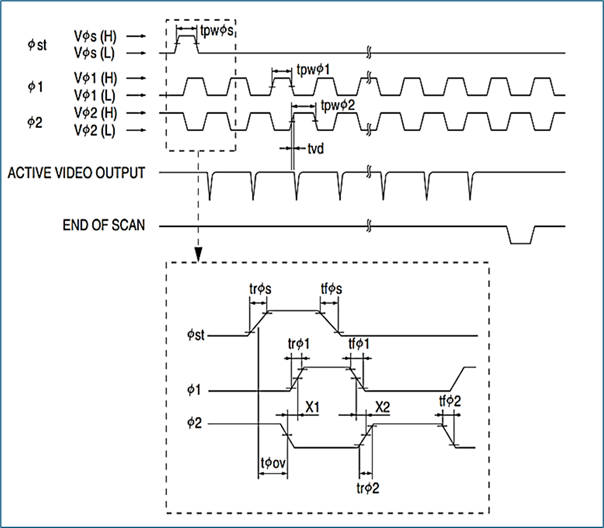
[3] Hamamatsu Photonics “Characteristic and use of NMOS Linear Image Sensors” K.K, Solid State Division, 2000.
[4] Nasir Alfara, “A review of charge-coupled device image sensors”, February, 2017.
[5] Jayadev Pradeep and S. V. Sunilkumar, “Solar Occultation Experiments (SOE) in the Venusian Atmosphere: effect of orbital parameters on the spatiotemporal distribution of measurements”, RASTAI, Advance Access publication June 28, 2, pp.324–344, 2023.
[6] T. Nakamura, K. Matsumoto, R. Hyuga and A. Yusa, “A NEW MOS IMAGE SENSOR OPERATING IN A NON-DESTRUCTIVE READOUT MODE”, IEEE Conference, CH2381-2/86/0000-0353, 1986.
[7] K. Tsujino, M. Akiba, and M. Sasaki, “A Charge-Integration Readout Circuit with a Linear-Mode Silicon Avalanche Photodiode for a Photon-Number Resolving Detector”, Basic and Advanced Research Department, National Institute of Information and Communications Technology, Koganei, Tokyo, Japan. 184–8795, 2007.
[8] Wei-Yu Chen2 and Chung-Yu Wu, ”A High Performance Linear Current Mode Image Sensor ”,IEEE, 978-1-4244-3828-0/09, 2009.
[9] Rudolph.H.Dyck, Gene.P.Weckler, ”Integrated Arrays of Silicon Photodetectors for Image Sensing”, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, April, Vol.15, No.4, 1968.
[10] G. P. Weckler, ”Storage mode operation of a phototransistor and its adaptation to integrated arrays for image detection”,e Internationl Electron Devices Meeting, Washington, D. October 1966; also Electronics, May 1, Vol.40, pp.75, 1967.
[11] M. A. Schuster and G. Strull, “A monolithic mosaic of photon sensors for solid-state imaging applications,” IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, December, Vol.13, pp.907-912, 1966.
[12] Meyer, Jerome. ”Solar occultation measurements with SCIAMACHY in the UV- visible-IR wavelength region.” PhD diss., Universit at Bremen, 2004.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




