Secured Framework for Electronic Medical Record Protection and Exchange Using Blockchain Technology
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v12i5.2834Keywords:
Blockchain Technology,, Electronic Medical Records,, Data Security and Privacy,, InteroperabilityAbstract
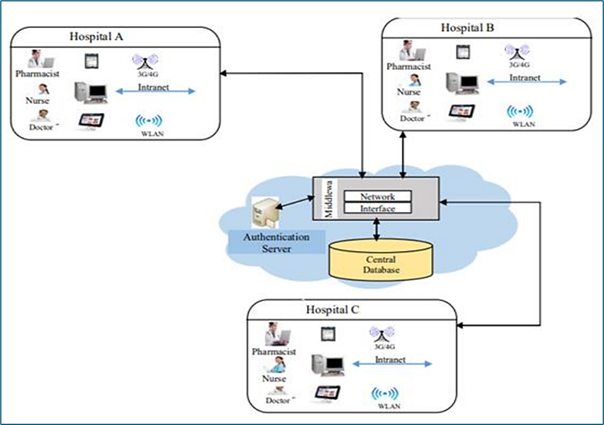
The adoption of blockchains to effectively manage medical services is fast becoming popular for professional use and in patient-centered applications. Electronic medical records are highly sensitive with user-privacy data online with clinical services that relate to patients’ diagnosis and treatments. The features of these medical records necessitate their availability, accessibility, agility, confidentiality and security. These have been demystified with the birth of the blockchain technology that seeks to proffer platforms and application services devoted to dependability and reliability amongst other features. Thus, we propose a blockchain health information framework for healthcare facilities. Our ensemble yields a permissioned blockchain using a hyper-fabric ledger. Using this state of technology on a peer-to-peer blockchain with various actors to include patient, practitioners and other users playing the roles of the creation, retrieval and storage of medical data for a patient to aid interoperability, our ensemble produce a query response time of 0.56 secs and https response time of 0.42 secs for 2500-users, and 0.78 secs and 0.63 secs respectively for 7500-users.
References
[1] I. Abu-elezz, A. Hassan, A. Nazeemudeen, M. Househ, A. Abd-alrazaq, " The benefits and threats of blockchain technology in healthcare: A scoping review," International Journal of Medical Informatics, Elsevier, Vol. 142, 104246, pp.1-9, 2020.
[2] H. Dang, T. T. A. Dinh, D. Loghin, E. Chang, Q. Lin, B. C. Ooi, "Towards Scaling Blockchain Systems via Sharding," In the Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Management of Data, ACM, 2019.
[3] G. Habib, S. Sharma, S. Ibrahim, I. Ahmad, S. Qureshi, M. Ishfaq, “Blockchain Technology: Benefits, Challenges, Applications, and Integration of Blockchain Technology with Cloud Computing. Future Internet,” MDPI 14 (11): 1-22, 14 (11), pp.1–22, 2022.
[4] M. J. H. Faruk, H. Shahriar, M. Valero, S. Sneha, S. I. Ahamed and M. Rahman, "Towards Blockchain-Based Secure Data Management for Remote Patient Monitoring," In the Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Digital Health (ICDH), Chicago, IL, USA, pp.299-308, 2021.
[5] A. Khatoon, “A Blockchain-Based Smart Contract System For Healthcare Management. Electronics,” MDPI, 9 (94), 2020.
[6] J. W. Kim, S.J. Kim, W. C. Cha, T. A. Kim, “Blockchain-Applied Personal Health Record Application: Development and User Experience,” Appl. Sci., MDPI, 12, 1847, 2022
[7] E. Kokoris-Kogias, P. Jovanovic, L. Gasser, N. Gailly, E. Syta and B. Ford, "OmniLedger: A Secure, Scale-Out, Decentralized Ledger via Sharding," In IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018.
[8] H. Li , X. Yang , H. Wang, W. Wei, W. Xue, “A Controllable Secure Blockchain-Based Electronic Healthcare Records Sharing Scheme,”. Journal of Healthcare Engineering,v Hindawi, pp.1-11, 2022.
[9] J. Liu, X. Sun, K. Song, “A Food Traceability Framework Based on Permissioned Blockchain. Journal of Cyber Security, 2(2), pp.107–113, 2020.
[10] S. Sayyad-Modi, R. K. Shingate, R. G. Jagtap, M. D. K., R. H. Sabale, “Smart Transfer Certificate Generator and Employer Verification Using Blockchain,” International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.11, Issue.6, pp.26-29, 2023.
[11] K. Saraf, “Fusing Blockchain and AI with the Metaverse: Unveiling the Future of Digital Transformation,” International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.11, Issue.9, pp.1-10, 2023.
[12] S. Nakamoto, “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,”, SSRN Product and Services, pp.1-9, 2008.
[13] E. Androulaki, A. Barger, V. Bortnikov, C. Cachin, K. Christidis, “Hyperledger Fabric: A Distributed Operating System For Permissioned Blockchains,” In the Proceedings of 13th EuroSys Conference, Article 30, pp.1-15, 2018.
[14] F. Armknecht, G. O. Karame, A. Mandal, F. Youssef, E. Zenner (2015). “Ripple: Overview and outlook,`` In Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Trust Trustworthy Computing, Heraklion, Greece: Springer, pp.163180, 2015.
[15] S. B. Far, M. R. Asaar, “A blockchain-based anonymous reporting system with no central authority: Architecture and protocol,” Cyber Security and Applications, Volume 2, 100032, Elsevier, pp.1-17, 2024.
[16] A. Wahrstatter, S. Khan, D. Svetinovic, “OpenFL: A Scalable and Secure Decentralized Federated Learning System on the Ethereum Blockchain,” Internet of Things, Vol. 00, Elsevier, pp.1–18, 2024.
[17] A. S. Balobaid, Y. H. Alagrash, A. H. Fadel, J. N. Hasoon, “Modeling of blockchain with encryption based secure education record management system,” Egyptian Informatics Journal, Vol.24, 100411, Elsevier, pp.1-11, 2023.
[18] A. Panwar, V. Bhatnagar, Manju. Khari, A. W. Salehi and G. Gupta (2022) A Blockchain Framework to Secure Personal Health Record (PHR) in IBM Cloud-Based Data Lake. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, Hindawi, Vol.2022, pp.1-19, 2022.
[19] G. Verma, N. Pathak, N. Sharma, “A Secure Framework for Health Record Management Using Blockchain in Cloud Environment,” Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1998 012019, 2021.
[20] S. Sabu, H. M. Ramalingam M. Vishaka, M. H. R. Swapna, S. Hegde, “Implementation Of A Secure And Privacy-Aware E-Health Record And Iot Data Sharing Using Blockchain,” Global Transitions Proceedings, Elsevier, Vol.2, Issue.2, pp.429–433, 2021.
[21] Dinh C. Nguyen, Pubudu N. Pathirana, Ming Ding; Aruna Seneviratne, “Integration of Blockchain and Cloud of Things: Architecture, Applications and Challenges,” IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, IEEE, Vol.22, Issue: 4, 2020.
[22] R. Sangeetha, B. Harshini, A.Shanmugapriya, T.K.P. Rajagopal, “Electronic Health Record System using Blockchain.” International Research Journal of Multidisciplinary Technovation, 1(2), pp.57-61, 2019.
[23] M. Usmana,. U. Qamar, “Secure Electronic Medical Records Storage and Sharing Using Blockchain Technology,” Procedia Computer Science, Elsevier, Vol.174, pp. 321–327, 2020.
[24] H. L Gururaj, A. M. Athreya, A. A. Kumar, A. M. Holla, S M Nagarajath, V. R. Kumar, “A New Era of Technology,” Wiley, pp.1-24, 2020.
[25] A. Ekblaw, j. D.. Azaria, M. D. Halamka, A. Lippman, “A Case Study for Blockchain in Healthcare: “MedRec” prototype for electronic health records and medical research data,” MIT Media Lab, 2016.
[26] D. Allenotor, D. A. Oyemade. “An optimized parallel hybrid architecture for cryptocurrency mining.” Computing, Information Systems, Development Informatics & Allied Research Journal; Vol.12, Issue 1, pp.94-104, 2022.
[27] A. Abayomi-Alli, A. J. Ikuomola,, I. S. Robert, O. O. AbayomiAlli, “An enterprise cloud-based electronic health records system.” Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology, 2(2), pp.21-36, 2014.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




