AI-based Model for Physio-Psycho Behavior of University Students
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v11i8.2328Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning, Artificial Neural Network, Physiological Parameters,, Psychological Parameters, YogaAbstract
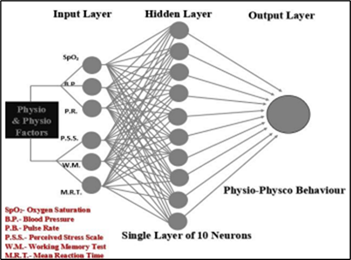
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful tool for measuring the psychophysiological behavior of students, enabling a deeper understanding of their cognitive and emotional states. By leveraging AI algorithms and data analytics, researchers can analyze various data sources such as facial expressions, voice tone, eye movements, and physiological signals to infer students` engagement levels, attention spans, stress levels, and overall emotional well-being. This technology has applications in educational settings, where AI can be utilized to develop intelligent tutoring systems that adapt to students’ individual needs, providing personalized feedback and interventions. Yoga and have gained significant popularity in recent years due to their potential positive effects on physical, mental, and emotional well-being. This research paper explores the effects of yoga on the psychological and physiological well-being of university students, using an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model. The study aims to analyze the relationship between regular yoga practice and various indicators of well-being among students. The ANN model is employed to uncover complex patterns and interactions within the dataset, providing insights into the potential benefits of these practices. The findings of this research have implications for promoting holistic well-being among university students. A sigmoid axon was used as a transfer function for input and output layers.
References
[1] P. Kora, K. Meenakshi, K. Swaraja, A. Rajani, and M. S. Raju, “EEG based interpretation of human brain activity during yoga and meditation using machine learning: A systematic review,” Complement Ther Clin Pract, Vol.43, pp.101329, May 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2021.101329.
[2] A. Toshev and C. Szegedy, “DeepPose: Human Pose Estimation via Deep Neural Networks,” in 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Jun., pp.1653–1660, 2014. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.214.
[3] K. Luu and P. A. Hall, “Examining the Acute Effects of Hatha Yoga and Mindfulness Meditation on Executive Function and Mood,” Mindfulness (N Y), Vol.8, Issue.4, pp.873–880, 2017, doi: 10.1007/s12671-016-0661-2.
[4] Y.-L. Ng, F. Ma, F. K. Ho, P. Ip, and K. Fu, “Effectiveness of virtual and augmented reality-enhanced exercise on physical activity, psychological outcomes, and physical performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials,” Comput Human Behav, Vol.99, pp.278–291, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2019.05.026.
[5] G. G. Chiddarwar, A. Ranjane, M. Chindhe, R. Deodhar, and P. Gangamwar, “AI-Based Yoga Pose Estimation for Android Application,” Int J Innov Sci Res Technol, Vol.5, Issue.9, pp.1070–1073, 2020, doi: 10.38124/IJISRT20SEP704.
[6] Y. Agrawal, Y. Shah, and A. Sharma, “Implementation of Machine Learning Technique for Identification of Yoga Poses,” in 2020 IEEE 9th International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies (CSNT), IEEE, Apr., pp.40–43, 2020. doi: 10.1109/CSNT48778.2020.9115758.
[7] M. H. B. de Moraes Lopes, D. D. Ferreira, A. C. B. H. Ferreira, G. R. da Silva, A. S. Caetano, and V. N. Braz, “Use of artificial intelligence in precision nutrition and fitness,” in Artificial Intelligence in Precision Health, Elsevier, pp.465–496, 2020. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-817133-2.00020-3.
[8] A. Garbett, Z. Degutyte, J. Hodge, and A. Astell, “Towards Understanding People’s Experiences of AI Computer Vision Fitness Instructor Apps,” in Designing Interactive Systems Conference 2021, New York, NY, USA: ACM, Jun., pp.1619–1637, 2021. doi: 10.1145/3461778.3462094.
[9] R. Kaplan-Rakowski, K. R. Johnson, and T. Wojdynski, “The impact of virtual reality meditation on college students’ exam performance,” Smart Learning Environments, Vol.8, Isuue.1, pp.21, 2021, doi: 10.1186/s40561-021-00166-7.
[10] Dm. Kishore, S. Bindu, and N. Manjunath, “Estimation of yoga postures using machine learning techniques,” Int J Yoga, Vol.15, Issue.2, pp.137, 2022, doi: 10.4103/ijoy.ijoy_97_22.
[11] V. Agarwal, K. Sharma, and A. K. Rajpoot, “AI based Yoga Trainer - Simplifying home yoga using mediapipe and video streaming,” in 2022 3rd International Conference for Emerging Technology (INCET), IEEE, May, pp.1–5, 2022. doi: 10.1109/INCET54531.2022.9824332.
[12] A. Dutta, M. Aruchunan, A. Mukherjee, K. G. Metri, K. Ghosh, and I. Basu-Ray, “A Comprehensive Review of Yoga Research in 2020,” Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine, Vol.28, Issue.2, pp.114–123, 2022, doi: 10.1089/jicm.2021.0420.
[13] S. Yao, “Construction of Relationship Model between College Students’ Psychological Status and Epidemic Situation Based on BP Neural Network,” Comput Intell Neurosci, vol. 2022, pp. 1–11, Feb. 2022, doi: 10.1155/2022/5115432.
[14] P. Li and F. Liang, “An Assessment and Analysis Model of Psychological Health of College Students Based on Convolutional Neural Networks,” Comput Intell Neurosci, vol. 2022, pp.1–10, 2022, doi: 10.1155/2022/7586918.
[15] J. L. Solas-Martínez, S. Suárez-Manzano, M. J. De la Torre-Cruz, and A. Ruiz-Ariza, “Artificial Intelligence and Augmented Reality in Physical Activity: A Review of Systems and Devices,” in Augmented Reality and Artificial Intelligence, pp.245–270, 2023. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-27166-3_14.
[16] P. L. Bhari and C. D. Kumawat, “A Study of Artificial Intelligence Education System and Traditional Education System,” International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.7, no.10, pp.124–129, 2019, doi: 10.26438/ijcse/v7i10.124129.
[17] A. Sharma and P. Singh, “Use of Artificial Intelligence for Healthcare Purposes: A Structured Review,” International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Open Access Review Paper, Vol.10, Issue.8, 2022, doi: 10.26438/ijcse/v10i8.2327.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




