An Approach to Build the Ergonomics of Interactive Software based on MDE
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v11i8.18Keywords:
Interactive Systems, Ergonomie, Models Transformation, Context-free Grammar, QVT Language, Software productivityAbstract
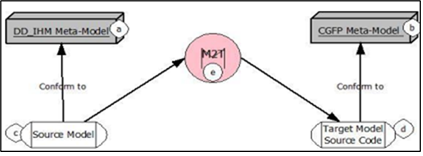
The design and implementation of interactive systems and Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI) use different techniques from both software engineering and ergonomics. To improve the productivity and quality of software, automating the development process is an important factor. User interfaces are nonfunctional but complex software components that play a vital role in the development of interactive applications. We propose in this paper an approach for the automatic production of Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI) for the development of interactive applications according to the Model-Driven Engineering (MDE) approach. A source Meta-Model called "DD_IHM" ("Description Diagram for Human-Machine Interfaces"), a target Meta-Model specific to the PHP language called "CGFP" (Context Grammar for PEAR) for the construction of HMIs and, a set of generic rules for transforming a model conforms to the source meta-Model into a model conforms to the target Meta-Model, written in the QVT language are develop. We apply this approach to the creation of a simple online registration platform.
References
[1] Hernández-López, Adrián, Colomo-Palacios, Ricardo, Et García-Crespo, Ángel, “Productivity in software engineering: A study of its meanings for practitioners: Understanding the concept under their standpoint”, In: 7th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI 2012). IEEE, pp.1-6, 2012.
[2] Abran, Alain, Al-Qutaish, Rafa E., et Cuadrado-Gallego, Juan J. “Analysis of the ISO 9126 on software product quality evaluation from the metrology and ISO 15939 perspectives.” WSEAS Transactions on Computers, Vol.5, no.11, pp.2778-2786, 2006.
[3] Anupriya et al., “Survey on Various Productivity Measures of Software Development Teams”, International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering 4(6), pp.462-464, June 2014
[4] Bindia Tarika, “Review on Software Analysis & Design Tools”, International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.8, Issue.1, pp.115-119, 2020.
[5] Rakesh Kumar, Priti Maheshwary, Timothy Malche, “Inside Agile Family: Software Development Methodologies”, International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.7, Issue.6, pp.650-660, 2019.
[6] Pfaff, Günther E. (Ed.). “User Interface Management Systems: Proceedings of the Workshop on User Interface Management Systems held in Seeheim”, Springer Science & Business Media, 2012.
[7] Schlungbaum, Egbert Et Elwert, Thomas. “Automatic User Interface Generation from Declarative Models.” In: CADUI. pp.3-17, 1996.
[8] Myers Brad A., “User Interface Software Tools”, ACM Transac-tions on Computer Human Interaction. Vol.1, no.2, pp.64-103, 1995.
[9] R. B. Hailpern , P. Tarr, “Model-driven development : The good, the bad and the ugly”, IBM Systems Journal, Vol.3, no.45, pp.1-25, 2006.
[10] Smita Agarwal, S. Dixit, Alok Aggarwal, “Model to Model Transformation for Declarative Models”, International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.6, Issue.11, pp.164-170, 2018.
[11] D. Schmidt, “Guest Editor`s Introduction:Model-Driven Engineering”, Computer, Vol.2, no.9, pp.25-31, 2006, ISSN 0018-9162.
[12] Warnars, H. L. H. S. “Object-oriented modelling with unified modelling language 2.0 for simple software application based on agile methodology” Behaviour & Information Technology, Vol.30, no.3, pp.293-307, 2011.
[13] Noulamo, T. & Tanyi, E. & Nkenlifack, Marcellin & Lienou, Jean-Pierre & Alain Bernard, Djimeli Tsajio. “Formalization method of the UML statechart by transformation toward Petri Nets.”, IAENG International Journal of Computer Science. 45. Pp.505-513, 2018.
[14] Tajouo, François & Noulamo, Thierry & Lienou, Jean-Pierre. “Procedure for the Contextual, Textual and Ontological Construction of Specialized Knowledge Bases”, European Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. 5. pp.62-67, 2021, doi:10.24018/ejece.2021.5.1.282
[15] André, Étienne, Choppy, Christine, et Noulamo, Thierry. “Modelling timed concurrent systems using activity diagram patterns”, Book Chapter, Springer International Publishing, pp.339-351, 2015.
[16] T. Noulamo, B. Fotsing Talla, M. Wane, L. H. Nzothiam Takou, “A Model-Driven Approach for Developing WEB Users Interfaces of Interactive Systems”, International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology (IJCTT) – Volume 68 Issue 4 pp.33-43, April 2020, ISSN: 2231-2803.
[17] A.J. Dix, J. Finlay, G. Abowd, R. Beale. “Human-Computer Interaction”, Prentice Hall, 1993.
[18] Scapin, Dominique Et Pierret-Golbreich, Christine. “Towards a method for task description: MAD Work with display units”, Elsevier Science Publishers, North-Holland, Vol.89, pp.371-380, 1989.
[19] D. Rix, H.R. Hartson. “Developing User Interfaces: Ensuring Usability Through Product Process”, Wiley Professional Computing John Wiley Sons, USA, 1993.
[20] Gray, Phil, England, David, et Mcgowan, Steve. Xuan: “Enhancing the UAN to capture temporal relation among actions.” People and Computers IX, pp.301-312, 1994.
[21] Fabio Patern. “Model-Based Design and Evaluation of Interactive Applications”, Springer, 2001.
[22] Hix, Deborah. “Generations of user-interface management systems.”, IEEE software, Vol.7, no.5, pp.77-87, 1990.
[23] Bass, Len, Faneuf, Ross, Little, Reed, et al. “A metamodel for the runtime architecture of an interactive system”. SIGCHI Bulletin, Vol.24, no.1, pp.32-37, 1992.
[24] Coutaz, J.. “Interfaces Homme-Ordinateur, Conception et Ralisation ”, Dunod Informatique, Paris, 1990
[25] Coutaz, Joëlle Et Nigay, Laurence. “Architecture logicielle conceptuelle des systèmes interactifs.” Analyse et conception de l’IHM, pp.207-246, 2001.
[26] Vasilakis, Christos, Lecznarowicz, D., Et Lee, Chooi, “Developing model requirements for patient flow simulation studies using the Unified Modelling Language (UML)”. Journal of Simulation, Vol.3, no.3, pp.141-149, 2009.
[27] Clerckx, T., Luyten, K., Coninx, K. “Generating Context-Sensitive Multiple Device Interfaces from Design.” In: Jacob, R.J., Limbourg, Q., Vanderdonckt, J. (eds) Computer-Aided Design of User Interfaces IV. Springer, Dordrecht, 2005, https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-3304-4_23.
[28] Nichols, Jeffrey & Myers, Brad & Higgins, Michael & Hughes, Joseph & Harris, Thomas & Rosenfeld, Roni & Pignol, Mathilde. “Generating remote control interfaces for complex appliances. UIST (User Interface Software and Technology)”, Proceedings of the ACM Symposium. pp.161-170, 2002, doi;10.1145/571985.572008.
[29] Booch, G., Rumbaugh, J., Jacobson, I. “Unified Modeling Language User Guide, The (2nd Edition)” (Addison-Wesley Object Technology Series). Addison-Wesley Professionnal, 2005
[30] France, Robert B., Kim, D.-K., Ghosh, Sudipto, et al. “A UML-based pattern specification technique“, IEEE transactions on Software Engineering, Vol.30, no.3, pp.193-206, 2004.
[31] Noulamo, T., Djimeli-Tsajio, A., Lienou, J. P., Fotsing-Talla, B. “Agent platform for the remote monitoring and diagnostic in precision agriculture.” Engineering Letter, Vol.30, Issue.3, pp.972–980, 2022.
[32] Bast, Wim; Murphree, Michael; Lawley, Michael; Duddy, Keith; Belaunde, Mariano; Gri_n, Catherine; Sendall, Shane; Vojtisek, Didier; Steel, Jim; Helsen, Simon; Tratt, Laurence; Reddy, Sreedhar; Ven-katesh, R.; Blanc, Xavier; Dvorak, Radek; Willink, “Meta Object Facility (MOF) 2.0 Query/View/Transformation (QVT) ”, Object Management Group, May 2011
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




