Seed Selection for Region-Growing Image Segmentation Based on Detected Keypoints
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v11i4.3038Keywords:
Region growing, seeds, image segmentation, keypoints detector, triangulations centersAbstract
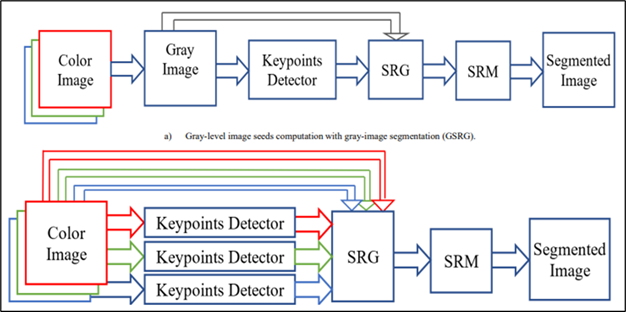
Seeded region growing (SRG) segmentation is utilized frequently in image processing, computer vision, and machine intelligence applications. The accuracy of the segmentation produced by the fundamental SRG algorithm relies on the proper seed selection. In this paper, seeds are allocated for each color component of the input image using a keypoint detector. Two methods for obtaining seeds are examined; the first method uses the keypoints as the seeds, while the second method uses the centers of the triangles constructed using the keypoints as the seeds for the SRG algorithm. After that, each color plane is subjected to the SRG algorithm, and the result is then concatenated. Subsequently, this segmentation is enhanced by employing a statistical region-merging algorithm. Several traditional keypoint detectors, such as SIFT, SURF, KAZE, and Harris, are compared and examined using the well-known Berkeley segmentation dataset (BSD) images. Finally, the provided technique is compared with two other approaches for image segmentation: K-means and mean shift.
References
[1] H. Mittal, A.C. Pandey, M. Saraswat, et al. "A comprehensive survey of image segmentation: clustering methods, performance parameters, and benchmark datasets.” Multimedia Tools Appl., Vol. 81, pp. 35001–35026, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10594-9
[2] Shaik Salma Begum, D. Rajya Lakshmi, “A Review of Current Methods in Medical Image Segmentation,” International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Vol.7, Issue.12, pp.67-73, 2019. https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v7i12.6773
[3] R. Yadav, M. Pandey, “Image Segmentation Techniques: A Survey." In: Gupta, D., Polkowski, Z., Khanna, A., Bhattacharyya, S., Castillo, O. (eds) Proceedings of Data Analytics and Management. Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies, Vol 90., pp. 231-239, 2022, Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-6289-8_20
[4] N. J. Wala`a, J. M. Rana, “A Survey on Segmentation Techniques for Image Processing," Iraqi Journal for Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Vol. 17, pp. 73-93, 2021, doi:10.37917/ijeee.17.2.10
[5] N. Zeitoun, M. Aqel, “Survey on image segmentation techniques”, Procedia Computer. Sci., Vol.65, pp. 797-806, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.09.027.
[6] R. Adams, L. Bischof, “Seeded Region Growing,” IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol. 16, No. 6, pp. 641-654, 1994. DOI:10.1109/34.295913
[7] M. Mousavi, F. Shariaty, M. Orooji, E. Velichko, “The performance of active-contour and 445 region growing methods against noises in the segmentation of computed-tomography scans,” in International Youth Conference on Electronics, Telecommunications and Information Technologies. Springer, Vol. 255, pp. 573–582, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58868-7_63
[8] M. Mancas, B. Gosselin, B. Macq, "Segmentation using a region-growing thresholding," Image Processing: Algorithms and Systems IV, Proc. SPIE Vol. 5672, (1 March 2005); https://doi.org/10.1117/12.587995
[9] J Borovec, J Kybic, A Sugimoto, “Region growing using superpixels with learned shape prior," Journal of Electronic Imaging, Vol.26, No. 6, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JEI.26.6.061611
[10] A. Callara, C. Magliaro, A. Ahluwalia, N. Vanello, “A Smart Region-Growing Algorithm for Single-Neuron Segmentation from Confocal and 2-Photon Datasets”, Front. Neuroinform,. Vol. 14:9, 2020. DOI: 10.3389/fninf.2020.00009
[11] O. Al-Furaiji, V. Rabtsevich, V. Tsviatkou, T. Kuznetsova, S. Chizhik, "Segmentation of AFM-Images Based on Wave Region Growing of Local Maxima," Engineering Letters, Vol. 28, no.3, pp. 681-698, 2020.
[12] N. Muhadi, A. Abdullah, S. Bejo, M. Mahadi, A. Mijic, “Image Segmentation Methods for Flood Monitoring System,” Water, Vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 1825, Jun. 2020, doi: 10.3390/w12061825.
[13] H. Wang, Y. Chen, "A smoke image segmentation algorithm based on rough set and region growing," Journal of Forest Science, Vol. 65, pp. 321-329, 2019. doi: 10.17221/34/2019-JFS
[14] X. Jiang, Y. Guo, H. Chen, Y. Zhang, Y. Lu, "An Adaptive Region Growing Based on Neutrosophic Set in Ultrasound Domain for Image Segmentation," IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 60584-60593, 2019, doi 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2911560.
[15] Y. Deng and B. S. Manjunath, “Unsupervised segmentation of color-texture regions in images and videos,” IEEE Trans. Pattern. Anal. Mach. Intell., vol. 23, no. 8, pp. 800-810, Aug. 2001.
[16] F. Jing, M. Li, H. J. Zhang, and B. Zhang, “Unsupervised image segmentation using local homogeneity analysis,” in Proc. Int. Symp. Circ. Syst., 2003. DOI:10.1109/ISCAS.2003.1206008
[17] J. Fan, D. K. Y. Yau, A. K. Elmagarmid, and W. G. Aref, “Automatic image segmentation by integrating color-edge extraction and seeded region growing,” IEEE Trans. Image Process., Vol. 10, no. 10, pp. 1454-1466, Oct. 2001.
[18] I. Imtiaz, I. Ahmed, M. Ahmad, K. Ullah, A. Adnan, M. Ahmad, "Segmentation of Skin Lesion Using Harris Corner Detection and Region Growing," 2019 IEEE 10th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, pp. 0614-0619, 2019. DOI: 10.1109/UEMCON47517.2019.8993034.
[19] F. Y. Shi, S. Cheng, “Automatic seeded region growing for color image segmentation,” Image Vis. Compt., vol. 23, pp. 877- 886, 2005.
[20] J. Fan, G. Zeng, M. Body, M. Hacid, “Seeded region growing: an extensive and comparative study," Pattern Recognition Letters, Vol. 26, Issue 8, Pages 1139-1156, 2005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2004.10.010
[21] L G. Ugarriza, E. Saber, S. R. Vantaram, V. Amuso, M. Shaw, R. Bhaskar, “Automatic image segmentation by dynamic region growth and multiresolution merging,” IEEE Trans. Image Process., Vol. 18, no. 10, pp. 2275-2288, Oct. 2009.
[22] C. -C. Kang and W. -J. Wang, "Fuzzy based seeded region growing for image segmentation," NAFIPS 2009 - 2009 Annual Meeting of the North American Fuzzy Information Processing Society, Cincinnati, OH, USA, pp. 1-5, 2009. DOI: 10.1109/NAFIPS.2009.5156397.
[23] A. Al-Faris, U. Ngah, N. Isa, I. Shuaib, “Breast MRI tumour segmentation using modified automatic seeded region growing based on particle swarm optimization image clustering.” In Proceedings of the Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer Verlag, Vol. 223, pp. 49–60, 2014.
[24] H. Tariq, T. Jilani, U. Amjad. S.M. Aqil Burney, “Novel Seed Selection and Conceptual Region Growing Framework for Medical Image Segmentation." BRAIN – Broad Research in Artificial Intelligence and Neuroscience, Vol. 10, Issue 1, 2019, ISSN 2067-3957.
[25] N. Tuan, X. Dai, T. Yurevich, “Multiple Seeded Region Growing Algorithm for Image Segmentation Using Local Extrema," Minsk, Belarus, January 2021.
[26] H. Shimodaira, "Automatic color image segmentation using a square elemental region-based seeded region growing and merging method." arXiv preprint, arXiv:1711.09352, 2017. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1711.09352
[27] N. Jothiaruna, K. Joseph Abraham Sundar, B. Karthikeyan, “A segmentation method for disease spot images incorporating chrominance in Comprehensive Color Feature and Region Growing.” Computer. Electron. Agric. Vol 165, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2019.104934
[28] J. Jiao, X. Wang, J. Zhang, Q. Wang, “Salient region growing based on Gaussian pyramid,” IET Image Process., Vol. 15, Issue 13, pp. 3142– 3152, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1049/ipr2.12307
[29] D. G. Lowe, "Distinctive image features from scale invariant keypoints," International Journal of computer vision, Vol. 60, no. 2, pp. 91–110, 2004.
[30] H. Bay, A. Ess, T. Tuytelaars, L. Van Gool, “Speeded-Up Robust Features (SURF),” Computer Vision and Image Understanding, Vol. 110, Issue 3, pp. 346-359, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2007.09.014
[31] P. F. Alcantarilla, A. Bartoli and A. J. Davison, “Kaze features,” European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, In: Fitzgibbon, A., Lazebnik, S., Perona, P., Sato, Y., Schmid, C. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2012. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, Vol 7577. pp. 214–227, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33783-3_16
[32] C. Harris, M. Stephens, "A Combined Corner and Edge Detector," Proceedings of the 4th Alvey Vision Conference, pp. 147-151, August 1988.
[33] P. Arbeláez, M. Maire, C. Fowlkes, and J. Malik, "Contour Detection and Hierarchical Image Segmentation," IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol. 33, no. 5, pp. 898-916, May 2011. DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.161.
[34] T. Malisiewicz, A. Efros, “Improving Spatial Support for Objects via Multiple Segmentations,” Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2007, University of Warwick, UK, September 10-13, 2007. ISBN 1-901725-34-0.
[35] Unnikrishnan, Ranjith, and Martial Hebert. “Measures of Similarity.” Seventh IEEE Workshops on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV/MOTION`05) – Vol. 1, pp. 394-394, 2005.
[36] R. Unnikrishnan, C. Pantofaru, M. Hebert, “Toward objective evaluation of image segmentation algorithms,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., Vol. 29, no. 6, pp. 929–944, Jun. 2007.
[37] S. K. Khan, A. Ahmad, “Cluster center initialization algorithm for k-means clustering," Pattern Recognition Letters, Vol. 25, Issue 11, pp.1293–1302, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2004.04.007.
[38] D. Comaniciu, P. Meer, "Mean shift: a robust approach toward feature space analysis," IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 603-619, May 2002. doi: 10.1109/34.1000236.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.




